- What is PLC?
- Advantages of PLC
- Disadvantages of PLC
- What is RTU?
- Advantages of RTU
- Disadvantages of RTU
- PLC and RTU Applications
- Difference between PLC & RTU
- PLC vs RTU
- Why PLC is better than RTU?
- Selecting Between PLCs and RTUs
- Which Conditions Are More Suitable for RTU or PLC?
- How is RTU connected to PLC?
- Why RTU is used in SCADA?
- Is RTU a suitable replacement for PLC?
- Conclusion
This article discusses the primary distinction between a PLC and an RTU.
| PLC – Programmable Logic Controller |
| RTU- Remote Terminal Unit |
The main difference between PLC and RTU is that PLC regulates the machine’s operation by monitoring input signals and outputs particular signals once pre-programmed instructions are executed.
While RTU gathers machine data and transmits it to a central place for analysis.
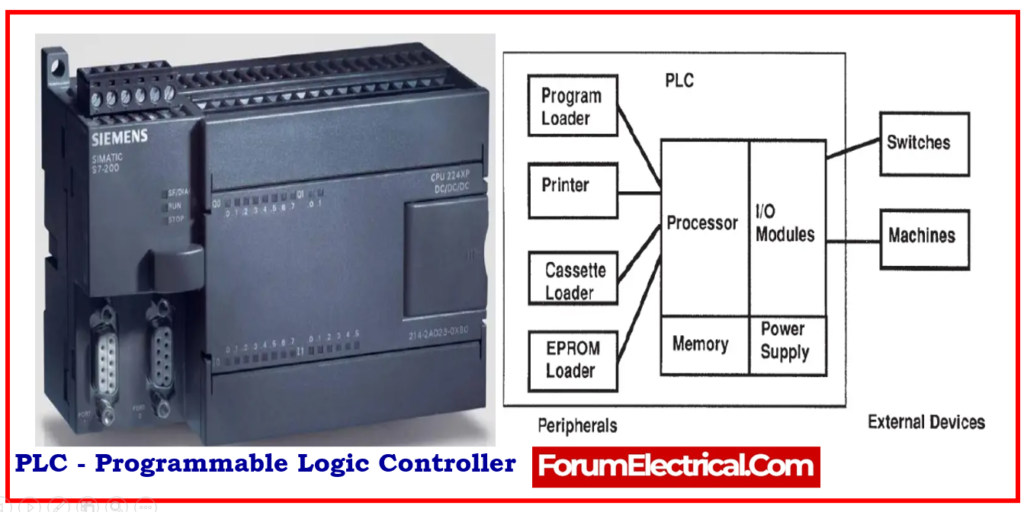
What is PLC?
PLCs are programmable logic controllers that are equipped with
- Digital inputs,
- Digital outputs,
- Analog inputs, &
- Analog outputs.
PLCs communicate through the communication protocols that have been embedded into them.
A software language, such as
- Ladder logic,
- Structured text,
- Instruction lists,
- Functional block diagrams, and so on,
is used to write the control logic in the controllers.
They are experienced in monitoring and automating complicated procedures. Process control is coded into PLCs, and this programmed runs in a loop.
They are therefore unable to identify changes in the signal within a specified time frame.
The PLC could regulate the outputs based on the logic contained in the controller, depending on the inputs received.
For communication between other control graphic systems, such as
- SCADA (or) HMI,
- Communication protocols
are utilized.
They can also communicate with other controllers.
PLCs are commonly found in the manufacturing & process industries.
In general, PLCs are utilized for controlling a process (or) sequence of processes, such as manufacturing or an assembly line.
Advantages of PLC
- PLC employs cutting-edge technology. As a result, it can perform functions such as timing, relay switching, counting, calculating, comparing, and so on.
- PLC communicates using established protocols.
- PLCs are more dependable than RTUs.
- A PLC control system makes it simple to upload & download applications. The PLC memory stores the program logic. As a result, there are no wiring issues.
- A PLC program can be edited, created, or deleted without rewiring.
- PLCs are simple to set up and use.
- PLC allows for quick operation while handling real-time results.
- PLC makes troubleshooting simple.
Disadvantages of PLC
- A trained operator is required for maximum efficiency and efficacy.
- The entire logic function is predetermined by the manufacturer & cannot be simply modified.
- PLCs require routine maintenance to keep them in excellent operating order.
- PLC is more expensive than RTU.
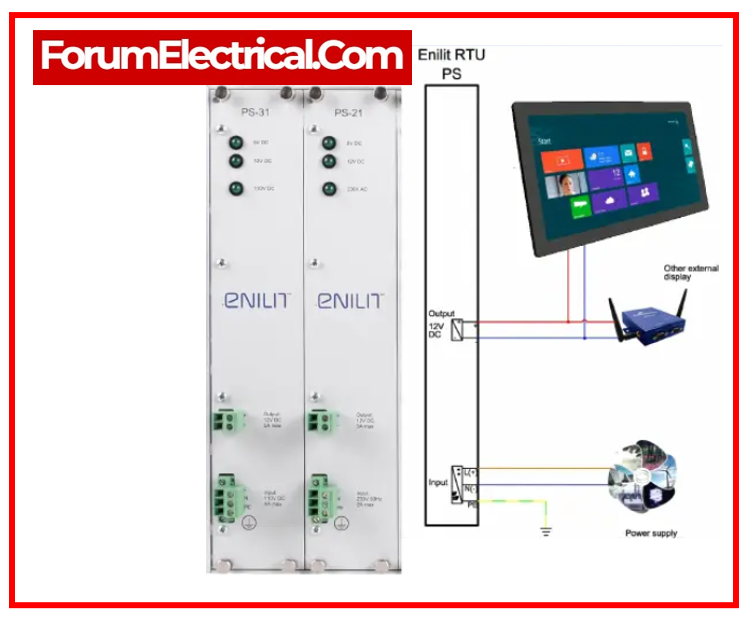
What is RTU?
The mobile terminal unit RTU (Remote Terminal Unit) is a small-sized PLC. A remote process is monitored and controlled by the RTU.
RTU is employed in industrial settings where the conditions are too extreme or dangerous for humans to be present.
RTU can also be used to monitor or control a process over a vast area. RTU can monitor & control all parameters such as
- Temperature,
- Pressure,
- Motor Speed, and so on.
They can also be used to activate or deactivate equipment based on predefined circumstances.
All signals are detected by these devices within the accurate time range, and they are recorded with time information.
Since they don’t lose signal, RTUs are typically chosen for applications requiring exact control.
Ex: They have the ability to promptly identify power disruptions and turn on backup power sources.
Advantages of RTU
- RTU consumes minimal power.
- RTU can function in severe settings.
- In circumstances when power consumption must be reduced, RTU can operate on event-triggered cycles. This means that RTU can only transfer data when a client request is received.
Disadvantages of RTU
- RTUs are costly to install & maintain.
- RTU employs outdated technology.
- In terms of processing power & data storage, RTU is not particularly impressive.
PLC and RTU Applications
Applications of PLC
- PLCs communicate with all forms of electric sensors, motors, field instruments, control valves, energy monitoring devices, and other automation equipment.
- PLCs are the central process control unit, or the workhorse of any industrial system.
- PLCs control operations such as DC motor speed control, liquid mixing, valve opening and closing, and control valve regulation.
- PLCs may also monitor and control temperature by reading analog signals from resistance temperature sensor.
Applications of RTU
- RTUs have applications in the remote data monitoring.
- RTUs, on the other end, collect data from faraway sites. RTUs collect data from equipment connected to a wide area network, such as wind turbines, solar panels, and water pumps.
- The data is then collected and delivered to a central location for further monitoring and analysis. The data can be utilized to mimic an alarm or to control distant devices.
Difference between PLC & RTU
PLC vs RTU
| Specifications | PLC | RTU |
| Power Usage | The energy consumption of PLCs is higher. | RTUs use a relatively small amount of energy. |
| Input Power | A PLC normally operates at 24 V DC (or) 230 V AC. Because PLC are often utilized in industrial settings & only required to function for a short span of time, they require minimal power. | Since RTU has limited programming control and no built-in display, SCADA is typically utilized with RTU. RTU demand more power since they must be powered for extended periods duration in order to track faraway areas. |
| Robustness | PLCs are less robust to severe environments and are less durable. | The Remote Terminal Unit (RTU) is known for its robustness & tolerance. Only the requested data & changes are transmitted via an RTU. |
| Program Driven Method | Programs are driven cyclically in a PLC. | Programs in an RTU are triggered by events, or in an event-driven method. |
| Data Transfer Speed | Because all of the programming and process data are transferred within a PLC, the data transfer speed in a PLC is faster than in an RTU. | When compared to a PLC, the RTU’s data transfer speed is slower. Only desired data and updates must be communicated in RTU. RTU transfers data more slowly as a result. |
| Hardware | PLCs are made up of a processor and several input & output devices that are linked to it. | An RTU can be a stand-alone device or one that is linked to a network of distributed controllers. |
| Data Communication | All of the programming and process data are exchanged within a PLC. | Any process voltage can be used with an RTU. |
| Programs & operating systems | A computer can be used to program a PLC. | Software that is confidential is used by RTU. Remote or on-site programming is possible with RTU. |
| Connectivity with SCADA | A PLC does not necessarily require a SCADA. | Since RTU lacks an internal display and has minimal programming control, SCADA is typically utilized with RTU. |
| Standards | PLC have communication standards like IEC61131-3 was established in response to their necessity. | RTU have communication standards like DNP3, IEC60870-5-104, IEC61850, IEC60870-5-101, and MQTT that were established in response to this necessity. |
| Language Used for Programming | Most PLCs are programmed using ladder logic. | RTUs employ platforms that are more configuration-driven. |
| Cost | PLCs have a higher cost than RTUs. | RTUs cost less than PLCs. |
| Feedback & Processing | PLC can be configured to do far more intricate computations, read many inputs at once, and make decisions in response to these inputs. | RTUs carry out simple computations by receiving a single sensor signal at a time & carrying out loop operations and several iterations throughout a program scan. |
| Protocol for Communication | It is preferable to employ PLCs in a certain setting. They do not require specific communication protocols as a result. The most essential consideration in PLC product communication is speed. PLCs therefore typically choose communication protocols including BACNET, ETHERCAT, ETHERNET IP, MODBUS, PROFIBUS, and PROFINET. | The majority of distributed SCADA systems use RTUs. Because sending personnel to the field to address potential faults (or) malfunctions in distributed structures raises operating expenses, remote terminal units (RTUs) are the perfect option in systems where data security and dependability are essential. |
Why PLC is better than RTU?
PLCs have better control over discrete operations and are quicker and more accurate than RTUs.
However, RTUs are more appropriate for controlling and monitoring several processes that are dispersed across a wide region remotely.
Selecting Between PLCs and RTUs
Recognize that both an RTU and a PLC have the ability to operate things to monitor input from the sensors when comparing their capabilities.
- PLCs are standalone controllers that are more compact, programmable, and used to run automated operations in a single, local plant.
- RTUs, on the other end, are designed to monitor under even the most extreme and widespread conditions, and they can be used for both local and wide-geographical equipment monitoring. They can also communicate remotely.
The key to choose one over the other is to comprehend their respective functions and application requirements.
Which Conditions Are More Suitable for RTU or PLC?
After learning more about the differences between an RTU and a PLC, it’s time to choose which one corresponds to your requirements.
These are some conditions when PLCs or RTUs are more appropriate.
Larger projects are usually more appropriate for PLCs, such as managing industrial assembly lines or the distribution of electrical power.
These kinds of large-scale controls are ideally suited for the PLC due to its robust computing capabilities.
However, an RTU is frequently a preferable choice if need to remotely operate and monitor equipment that is located in a more remote area, such solar power systems or wind turbines.
These kinds of projects are more appropriate for the RTU because of its additional features, which include data logging & communication protocols.
How is RTU connected to PLC?
RTU is comparable to a remote PLC in that data is transmitted from it to the primary PLC when its IOs have been configured.
This controller’s data is then transmitted to SCADA systems (or) any other more advanced level graphics control system through RTU.
Why RTU is used in SCADA?
The sensors are interfaced with the SCADA Master Station (or) Communications Network through a remote terminal unit, or RTU.
RTUs offer certain local control functions and telemetry data. They are not the same as PLCs, or programmable logic controllers.
These electronic devices are controlled by microprocessors.
Is RTU a suitable replacement for PLC?
RTUs assist you in monitoring the most essential operations so that you can react quickly in the event that something goes wrong.
For remote sites, RTUs offer a more affordable alternative to PLCs and PLRs while however providing a comparable degree of automation and information.
They are employed in transport, communications, and networking processes.
When compared to a SCADA PLC, an RTU is typically stronger and has greater capacities for monitoring and control.
Because of this, SCADA RTUs perform better in settings where a large number of objects need to be managed and monitored.
While professional users may gain advantages from PLC customization, others might choose to acquire an RTU specifically made for their monitoring & control scenario.
Devices known as RTUs are made to be installed in remote locations in order to track and report on events that take place there. Since they provides the same degree of automation and information at remote locations as PLCs, they are frequently utilized as a more affordable option.
The following are some advantages of using RTUs:
- An RTU has a greater “heavy-duty” than a PLC. Compared to PLCs, they are capable of more monitoring and control. Thus, when it comes to monitoring and controlling a wide variety of devices, RTUs are better than PLCs.
- The manufacturer programs them, therefore programming proficiency is not an issue. It will be simpler and quicker to train new hires. But keep in consideration that you may easily find a vertically integrated organization that can create a solution specifically customized to your needs if you require a unique design to address particular issues.
- Furthermore, even in the absence of a master station’s direct involvement, RTUs are capable of managing several processes. The specialty in networking, communications, & transportation processes is one of these procedures.
- Because of its wireless communication capabilities, RTUs are more suited for application across larger geographic areas.
Conclusion
There are two types of controllers used to handle machines in the industrial world:
- Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC) &
- Remote Terminal Units (RTU).
While each serves a distinct purpose, many individuals are unaware of the differences.
A PLC is the best solution if you need to operate machines by reading the input signals & executing programming.
An RTU is the best solution if you require it to collect the data from equipment and deliver it to an overview for analysis.