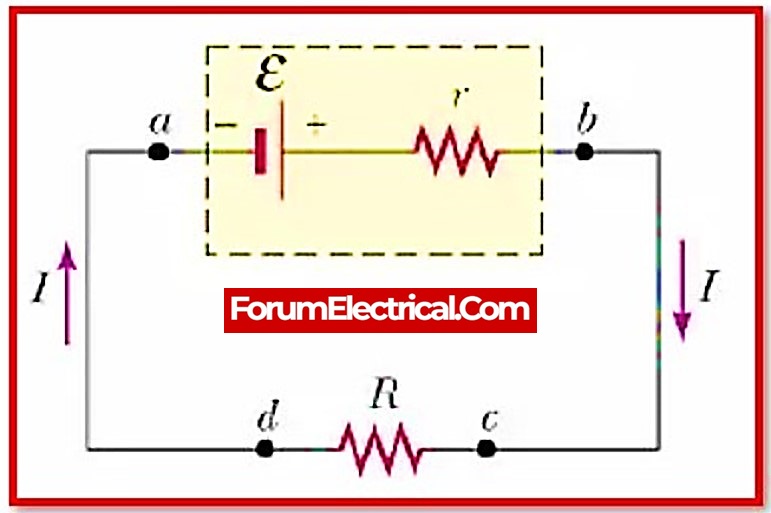
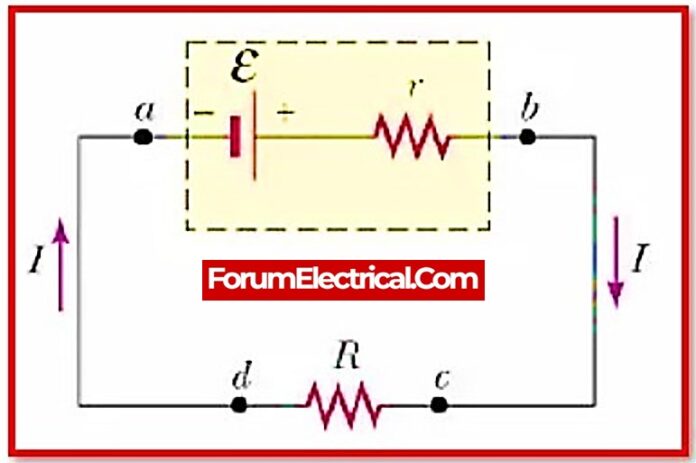
DC Circuit Rule is a principle in electrical engineering that describes the relationship between the current, voltage, and resistance in a direct current (DC) circuit. It states that the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the two points, and inversely proportional to the resistance between them. This relationship is described by Ohm’s Law, which can be expressed mathematically as:
I = V/R
where:
I – Current through the conductor (A)
V – Voltage across the conductor (V)
R – Resistance of the conductor (Ω)
Ohm’s Law is a fundamental principle in electrical engineering and is used to predict the behavior of DC circuits. It is based on the idea that the current through a conductor is determined by the resistance of the conductor and the voltage applied across it.
The DC Circuit Rule is only applicable to DC circuits. It is not applicable to alternating current (AC) circuits, which behave differently due to the changing nature of the current. The DC Circuit Rule is also only applicable to linear circuits, which obey Ohm’s Law. Nonlinear circuits, such as those containing diodes or transistors, do not obey Ohm’s Law and cannot be analyzed using the DC Circuit Rule.