Diesel Generator
Diesel generators are essential for providing backup and emergency power to industrial, commercial, & residential sectors.
- Diesel Generator
- 1). Engine Fails to Start
- 2). Engine Starts but Shuts Down Immediately
- 3). No (or) Low Voltage Output
- 4). Engine Overheating
- 5). Black Smoke from Exhaust
- 6). White Smoke from Exhaust
- 7). Abnormal Engine Noise
- 8). Excessive Vibration
- 9). Battery Not Charging
- 10). Oil Leakage
- Preventive Measures
- Conclusion
However, they are prone to a variety of operational issues caused by
- Mechanical,
- Electrical, or
- Fuel-related failures.
Understanding the problem warning signs and taking the appropriate repair procedures ensures that the generator operates reliably and safely.
This post outlines common issues seen in DG sets, what causes them, and how to effectively handle them. The common problems are:
1). Engine Fails to Start
2). Engine Starts but Shuts Down Immediately
3). No (or) Low Voltage Output
4). Engine Overheating
5). Black Smoke from Exhaust
6). White Smoke from Exhaust
7). Abnormal Engine Noise
8). Excessive Vibration
9). Battery Not Charging
10). Oil Leakage
1). Engine Fails to Start
The DG set fails to start. No ignition (or) combustion happens. The system stays fully idle, with only the starter clicks.

Possible Causes
- The battery is dead (or) undercharged.
- Low (or) no fuel in tank.
- Air lock in fuel line.
- Starter motor failed.
- loose (or) corroded cable connections.
Solutions
- Charge (or) replace the battery.
- Fill the fuel tank with clean diesel.
- Bleed air from the fuel system.
- Check, repair, or replace the starter motor.
- Inspect and tighten each cable terminal.
2). Engine Starts but Shuts Down Immediately
The DG engine starts but shuts off after a few seconds. If resumed, the cycle may repeat itself. This indicates a protection trip (or) an immediate system malfunction.
Possible Causes
- Low oil pressure triggers protective shutoff.
- High engine temperature.
- Faulty temperature (or) oil pressure sensor.
- Water (or) pollutants in fuel.
Solutions
- Top up engine oil to the necessary level.
- Inspect and maintain the cooling system.
- Replace the malfunctioning sensors.
- Drain and refill the gasoline tank with clean fuel.
3). No (or) Low Voltage Output
The engine runs normally, but the generator does not deliver voltage, or the output voltage is much lower than rated. Loads may not function or receive unsteady power.
Possible Causes
- Automatic Voltage Regulator (AVR) fault.
- Damaged (or) shorted alternator windings.
- A blown fuse (or) circuit breaker triggered.
- loose electrical connections in control panel.
Solutions
- Replace (or) calibrate the AVR.
- Test the alternator & rewind if needed.
- Replace a fuse or reset the breaker.
- Tighten the terminal connections.
4). Engine Overheating
An unexpected rise in temperature during operation. Alarms or trips may be triggered.
Steam, high gauge readings, and coolant boil-over are all potential visual signs.

Possible Causes
- Low coolant level.
- Clogged radiator fins.
- Malfunctioning water pump (or) thermostat.
- Overloading the generator.
Solutions
- Refill the coolant to the required level.
- Clean the radiator with the compressed air (or) water.
- Replace the defective pump or thermostat.
- Reduce the connected electrical load.
5). Black Smoke from Exhaust
Exhaust generates thick black smoke while in operation. This indicates incomplete combustion or a high fuel mixture. Engine efficiency decreases noticeably.

Possible Causes
- Dirty or blocked air filter.
- Excessive fuel delivery (rich mix).
- Improper injector spray or timing.
- Restricted exhaust system.
Solutions
- Clean (or) replace the air filter.
- Adjust the fuel injection timing.
- Service (or) replace the fuel injectors.
- Inspect & clean exhaust outlets.
6). White Smoke from Exhaust
White or light-grey smoke occurs during starting or continuous operation. Frequently accompanied by loud running or knocking sounds.
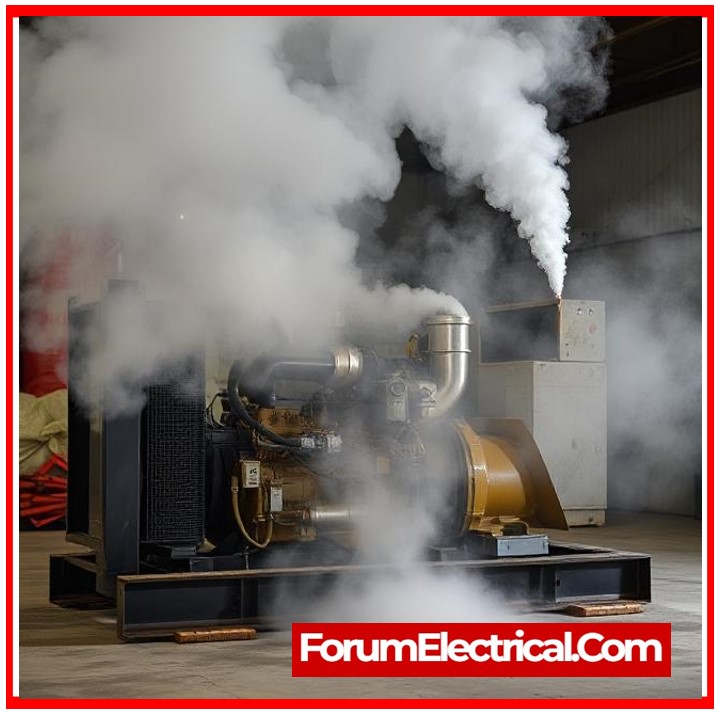
This suggests water intrusion or insufficient compression.
Possible Causes
- Water in diesel fuel.
- Low cylinder compression.
- Faulty head gasket.
Solutions
- Drain the polluted fuel & clean the tank.
- Perform a compression test; change worn piston rings as needed.
- Replace the blown head gasket.
7). Abnormal Engine Noise
Unusual knocking, grinding, (or) rattling sounds from the engine (or) alternator. May increase with load (or) speed.
This indicates an internal mechanical fault (or) loose components.
Possible Causes
- Loose engine bolts (or) components.
- Damaged crankshaft (or) connecting rod bearings.
- Incorrect valve clearance.
- Timing gear wear.
Solutions
- Tighten all available bolts and mounts.
- Inspect the crankshaft bearings for wear.
- Adjust valve clearance to specs.
- Replace the worn timing components.
8). Excessive Vibration
DG set shakes more than usual during operation. It is possible to create instability, component damage, (or) structural fatigue.
Possible Causes
- Unbalanced load between generator stages.
- Misalignment of engine and alternator.
- Worn-out anti-vibration pads (or) mounts.
Solutions
- Balance the weight evenly across all phases.
- Realign the alternator shaft using a dial gauge.
- Replace the vibration isolation mounts.
9). Battery Not Charging
The battery voltage does not increase during operation. Start-up failures occur frequently. The charge indication stays low.

The alternator may not be capable of delivering charging current.
Possible Causes
- Alternator failure.
- Loose (or) broken belt.
- Corroded Battery Terminals.
Solutions
- Replace the alternator if it is defective.
- Tighten (or) replace the driving belt.
- Clean the battery terminals and add petroleum jelly.
10). Oil Leakage
Oil drops or streaks on engine parts, crankcase or ground. Alarms or shutdowns may occur due to low oil levels.
Frequently causes environmental and fire dangers.

Possible Causes
- Overfilled oil reservoir.
- Damaged (or) worn-out gaskets & seals
- Loose oil drain plug.
Solutions
- Decrease oil level to the acceptable range.
- Replace the faulty gaskets and seals.
- Tighten the drain plug securely.
Preventive Measures
- Conduct daily checks on gasoline, oil, & coolant levels.
- Follow the OEM’s maintenance intervals for filters, fluids, & belts.
- Load testing involves operating the DG under actual load conditions on a periodic basis.
- Keep a generator logbook to track problem trends and repair history.
- Keep the battery terminals clean & maintain correct electrolyte levels.
Conclusion
Understanding diesel generator faults & their symptoms is essential for efficient and accurate troubleshooting.
Promptly identifying and correcting these faults not only restores DG operation, but also prevents future breakdowns and extends equipment life.
Field technicians and site managers must be alert and aggressive in their maintenance processes to ensure that their diesel generators provide uninterrupted electricity.









