Kirchhoff’s Laws include two fundamental principles in electrical circuit analysis:
- Kirchhoff’s Current Law (KCL) (Kirchhoff’s First Law or Kirchhoff’s 1st Law) &
- Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law (KVL) (Kirchhoff’s Second Law or Kirchhoff’s 2nd Law).
These principles serve as essential tools for evaluating complicated electrical circuits, allowing engineers & researchers to predict & comprehend the behavior of circuits in various configurations. Kirchhoff’s Laws are widely applied in
- Electronics engineering,
- Electrical engineering, &
- Physics for circuit analysis & design.
What does Kirchhoff’s Current Law (KCL) State?
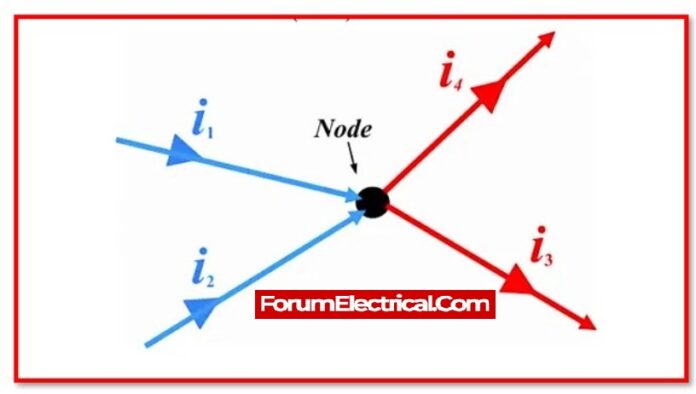
Kirchhoff’s current law states that the algebraic sum of current entering into a node (or) a loop must be equal to the algebraic sum of current flowing out of it.

What is Node?
A node is a junction, connector, or terminal in a circuit that connects two or more branches by joining or connecting circuit components. A dot represents a node.
In an electrical circuit, the term “Node” typically refers to
the joining or intersecting of two or more components, such as cables, that conduct current. A closed circuit path is also necessary for current to flow through a node, either in or out.
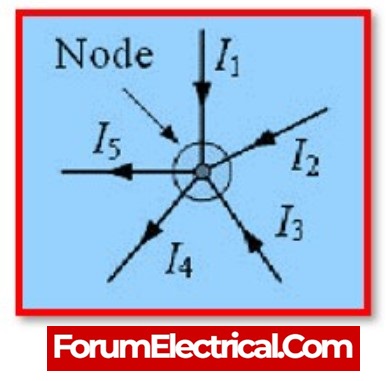
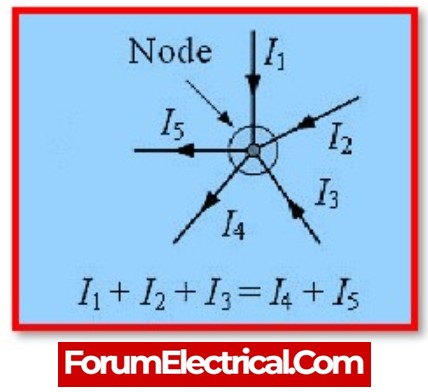
According to the node currents from the above diagram,
The 3 currents entering the node in this case,
- I1, I2, and I3 all have positive values, whereas
- I4 and I5 have negative values,
the two currents leaving the node.
As a result, the equation can also be rewritten,
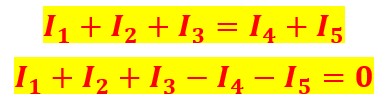
What is the other name of Kirchhoff’s Current Law?
Kirchhoff’s Current Law is also called as Kirchhoff’s First Law.
Application of KCL:
KCL is used to calculate the amount of current passing through each electronic component in a circuit. By adjusting the component’s resistance, we can alter the component’s current according to KCL law.