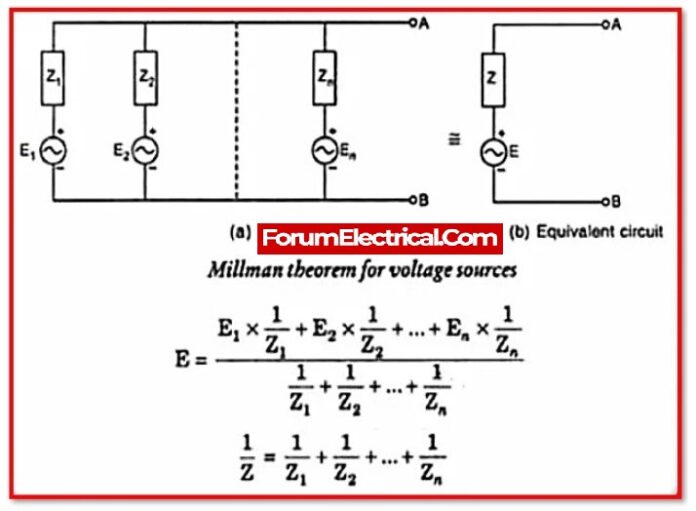
Millman’s Theorem is a principle in electrical engineering that allows the complex impedance of a series of resistors and voltage sources to be reduced to a single equivalent impedance. It states that any series circuit consisting of a number of resistors and voltage sources can be represented by an equivalent circuit consisting of a single resistor in parallel with a single voltage source. The resistor is the equivalent resistance of the circuit, and the voltage of the source is the equivalent voltage of the circuit. Millman’s Theorem is named after the American engineer Jacob Millman, who first proposed it in the mid-20th century.
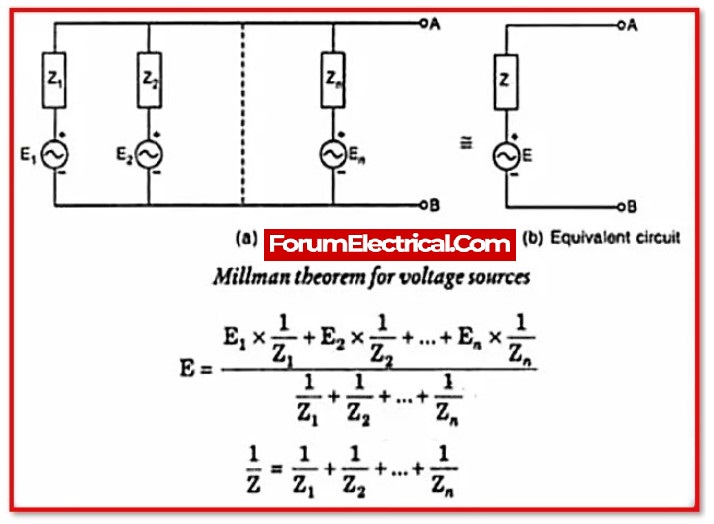
To determine the equivalent resistance and voltage of a series circuit using Millman’s Theorem, the following steps can be followed:
- Divide the circuit into a number of branches, each containing a single resistor and voltage source.
- Calculate the equivalent resistance and voltage of each branch.
- The equivalent resistance of the circuit is the sum of the individual branch resistances.
- The equivalent voltage of the circuit is the sum of the individual branch voltages.
- Millman’s Theorem is a useful tool for analyzing and designing series circuits because it allows the circuit to be represented by a single, simplified model. This makes it much easier to understand the behavior of the circuit and to calculate its response to different input signals.
Millman’s Theorem is only applicable to series circuits consisting of resistors and voltage sources. It is not applicable to circuits with other types of elements, such as inductors or capacitors. It is also not applicable to nonlinear circuits.
What is the outcome of Millman’s theorem?
It is an incredibly useful theorem for determining the voltage across the load and the current flowing through the load. It’s also known as the parallel generator theorem. A combination of voltage and current sources with parallel connections can be reduced to a single equivalent voltage (or) current source.
Millman’s Theorem Applications:
- Millman’s theorem is particularly useful for determining the voltage and current of load impedance when a large number of parallel branches are available with a variety of voltage sources.
- This theorem is simple to calculate. It does not necessitate the use of additional equations.
- This theorem is used to solve complex circuits with complex elements such as Op-Amps.
Millman’s theorem Limitations:
- This theorem does not apply to a circuit with a dependent source connected to an independent source.
- This theorem is useless for circuits with less than two independent sources.
- This theorem does not applicable to a circuit composed entirely of series parts.
- This theorem is inapplicable when there is an element connected between the source and the destination.