- Nominal Voltage
- Rated Voltage
- Operating Voltage
- Nominal Voltage v/s Rated Voltage
- Nominal Voltage v/s Operating Voltage
- What is the nominal voltage of a battery?
- What is nominal voltage of an electric motor?
- Difference between Nominal voltage, Rated Voltage and Operating Voltage
- Nominal Voltage vs Rated Voltage vs Operating Voltage
In the field of electrical engineering, users regularly come into the three voltage ratings that are listed below in relation to electrical equipment & power systems:
1). Nominal Voltage
2). Rated Voltage
3). Operating Voltage
Here we will go through these three concepts in relation to the voltage rating of various electrical systems.
Nominal Voltage
Nominal voltage is also known as named voltage. The voltage value given to an electric circuit (or) system to denote its voltage class is specified as the nominal voltage.
In layman’s terms, the voltage level of an electrical power system is referred to as the system’s nominal voltage. It is also called as system voltage.
In a power system, typical nominal voltages include 440 V, 11 kV, 33 kV, 66 kV, 110 kV, 132 kV 230 kV, 400 kV, and 765 kV.
When designing any electric equipment, the designer must first examine the nominal voltage rating of the system (network) on which the equipment will be used.
For safety areas, a tolerance of 10% or greater is also used.
Essentially, the nominal voltage does not correspond to the specific operational voltage of the device. It is just a voltage value used to designate or refer to an electrical equipment.
As a result, the actual voltage (in volt) at which the device functions may differ from the nominal voltage within a voltage range that permits the device to function well.
In application, nominal voltage is mostly utilised as a voltage reference for specifying electrical device and system ratings.
It is the supply system voltage to which the gadget may be attached. As a result, we may regard the nominal voltage as an approximation of a system’s voltage level.
Rated Voltage
The rated voltage of electrical equipment is the value of the system voltage (in volt) at which the equipment is intended to function safely and reliably.

As a result, the rated voltage of electrical equipment(system) is the highest voltage at which the device can work without being harmed and demonstrates its projected performance.
The voltage tolerance range is determined such that it is within the rated voltage range.
The rated voltage (in volts) is always stated on the equipment’s nameplate.
For example, the rated voltage of a 1phase induction motor is indicated on the nameplate as 240 V 10%, which implies the motor may work safely within the voltage range of 220 V to 264 V.
As a result, if the motor is run within this voltage range, it will perform reliably.
It should be remembered that the rated voltage must be larger than the nominal voltage in order for the device to work properly.
The difference between the rated voltage and the nominal voltage must be significant enough so that fluctuations in the nominal voltage in the power line (transmission line) can be readily evaluated.
As a result, can deduce that the rated voltage of an electrical device is the maximum voltage at which it can work without being destroyed.
Operating Voltage
The actual magnitude of the supply voltage that is supplied to the terminals of the equipment is referred to as the operational voltage.
To put it another way, the voltage at which an item of machinery is being operated is referred to as the operational voltage of the machinery.
- Voltmeters,
- Multimeters, and
- Other instruments
designed specifically for measuring voltage are often used in the process of determining an equipment’s operational voltage.
In order to guarantee that the equipment may be used in a manner that is secure, dependable, and cost-effective, it is imperative that the operating voltage not be higher than the rated voltage.
If the operating voltage is outside of the range of the rated voltage, then the functioning of the equipment will be negatively impacted, and it is also possible that the equipment could be damaged as a result.
Nominal Voltage v/s Rated Voltage
Nominal voltage is an electrical power system’s voltage. It is also called as system voltage. Nominal voltage in 3-phase systems is the voltage between external lines.
The equipment’s rated voltage range is where it operates reliably and stably.
For equipment to operate within rated voltage, the device designer should consider the voltage safety margin.
To ensure equipment safety, the rated voltage must exceed the nominal voltage. To examine power line nominal voltage changes, the nominal-rated voltage differential must be significant.
Consider a circuit breaker circuit works to determine rated voltage. Electrical circuit breakers are switching devices that govern and safeguard electricity systems. A circuit breaker’s insulating scheme determines its rated voltage.
A circuit breaker’s rated maximum voltage is its greatest RMS voltage. The circuit breaker’s maximum operating voltage is this number. kV RMS is the rated voltage.
The circuit-“rated breaker’s voltage” is the highest voltage it can safely interrupt without arcing.
Nominal Voltage v/s Operating Voltage
Operating voltage is the voltage at which the equipment(device) works. For equipment to work reliably, it must be run within its rated voltage range. The actual voltage applied to the equipment terminal is the operating voltage.
A multimeter (measuring device) is used to measure the voltage at an equipment terminal. If the voltage applied is greater (or) lower than the equipment’s rated voltage, the equipment won’t work as well.
Example
For a 132 kV power system, the following information is provided on the installation of a circuit breaker. The functioning of the equipment might be negatively impacted if the operating voltage is beyond the range of the rated voltage.
Nominal Voltage–Ranges 132 kV
Rated Voltage –Rated 132 kV +/- 10 % [118.8 kV– 145.2 kV ]
Operating Voltage –Operation Range of 118.8 kV to 145.2 kV.
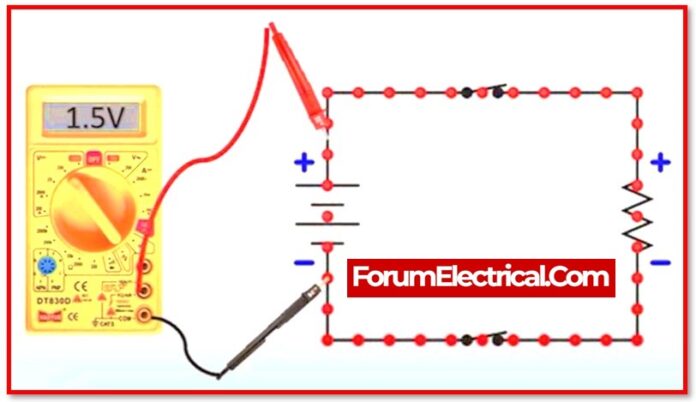
What is the nominal voltage of a battery?
A battery is an electrochemical device that creates a voltage potential by immersing metals with varying affinities in acid.
Example
A battery with an actual voltage of 1.62 V may be referred to as a “1.5-volt battery,” implying that the battery has the nominal voltage range of 1.5 V. Another example is the word “DC 12V,” which refers to a 12V battery, whether fully charged (13.7 Vdc) (or) discharged (10Vdc).
What is nominal voltage of an electric motor?
Even though it is possible to run the motor with a voltage that falls anywhere within the range that is provided, the motor should be operated at the nominal voltage. This is the recommended voltage at which the electric motor should be operated.
In the case of DC motors, the nominal voltage is an important parameter. The torque-speed curve of a motor is, in point of fact, determined by the motor’s nominal voltage.
Difference between Nominal voltage, Rated Voltage and Operating Voltage
Nominal Voltage vs Rated Voltage vs Operating Voltage
| S.No | Specification | Nominal Voltage | Rated Voltage | Operating Voltage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Definition | The voltage value of electrical equipment (device) intended for usage is referred to as nominal voltage. | The maximum (maximal) voltage that can be safely applied to equipment is referred to as rated voltage. | The operational voltage is the voltage value at which equipment (device) is operated. |
| 2 | Voltage Tolerance | For safety areas, a tolerance of 10% ± 10% (or) higher is also used. | The voltage tolerance range has been determined to be within the rated voltage range. | For safe operation, the operating voltage tolerance is within the rated voltage range. |
| 3 | Performance | As a voltage reference, nominal voltage is used, and it is considered a “approximate” voltage level. | To function safely, the rated voltage must exceed the nominal voltage. | The operational voltage is the voltage actually applied to the terminal of the equipment. |
| 4 | Capability | The total amount of voltage that the equipment are capable of handling is denoted by the nominal voltage. | The resistance rate characterises the rated voltage, while the resilience (capability to withstand) is expressed in % rate. | Operating voltage refers to the voltage at which they are run at the present time. |
| 5 | Typical Representation | Ranges 132 kV | Rated 132 kV +/- 10 % [118.8 kV– 145.2 kV ] | Operation Range of 118.8 kV to 145.2 kV |