- What is meant by the term “Plum Pudding Model”?
- Background and history of plum pudding model
- Function of Electron in Plum Pudding Model
- Thomson’s atomic model Postulates (Statement)
- Characteristics of the Plum Pudding Model (Thomson’s atomic model)
- Advantages of Plum Pudding Model
- Disadvantages (Limitations) of Plum Pudding Model
- What is the charge of the pudding component?
- What were the reasons for the failure of Thomson’s model of the atom?
- Replacement of the Plum Pudding Model
- Why did Rutherford invalidate JJ Thomson’s model?
- Conclusion
What is meant by the term “Plum Pudding Model”?
The plum pudding model, or Thomson’s plum pudding model, is a historical scientific model of the atom.
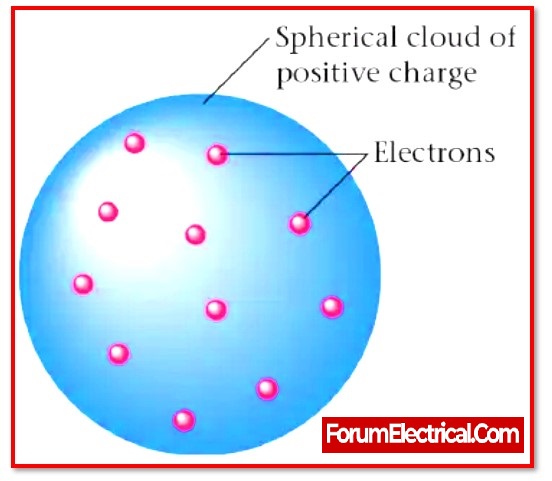
It is also called as the plum pudding model. The electrons in the plum pudding model are surrounded by the volume of positive charge, much as positively-charged “plums” are embedded in a negatively-charged “pudding.”
This is how the plum pudding model is characterised .
Background and history of plum pudding model
Following the discovery of the electron, yet prior to the discovery of the atomic nucleus, the English physicist Sir Joseph John J.J. Thomson came up with the initial version of the plum pudding model.
He called it the “plum pudding model.”
The concept attempted to explain two characteristics of atoms that were common knowledge at the time:
- The fact that electrons are particles with a negative charge and
- The fact that atoms do not have a net electric charge.
The name “corpuscles” was given to these negatively charged particles by J.J. Thomson at the time of their discovery.
The atomic structure of matter was first represented by Thomson’s Plum Pudding Model, which was the first model to be represented.
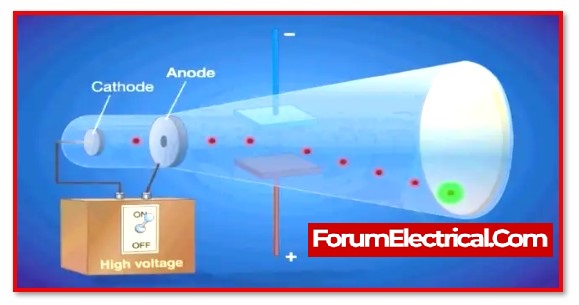
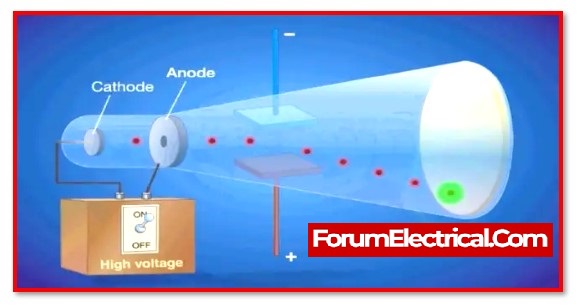
He made use of a device known as a cathode ray tube, which expelled particles from atoms.
He discovered that there were electron particles with a negative charge because of the direction in which they travelled towards a positive charge.
Function of Electron in Plum Pudding Model
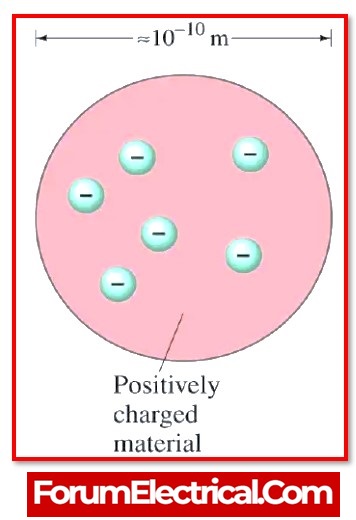
The Plum Pudding Model proposes that a material may be thought of as being composed of several little spheres, each of which has a radius that is around 10–10 m in diameter.
A positive charge is distributed evenly across the whole of the sphere-shaped volume known as pudding.
The particles that have the negative charge known as plums are the name given to the electrons that are scattered as point charges in the shells.
The force is applied to electrons that have a negative charge by a sphere that has a positive charge.
The net force that is exerted on electrons with a negative charge by a sphere that has a positive charge is directed in the direction of the sphere’s centre.
These electrons with negative charges are repelled by one another, which results in the formation of shells.
Thomson’s atomic model Postulates (Statement)
Postulate-1: An atom is a positively charged sphere that contains electrons.
Postulate-2: An atom as a whole is the one electrically neutral because of the magnitudes of the negative & positive charges are equal.
Characteristics of the Plum Pudding Model (Thomson’s atomic model)
- The electrons that make up an atom are enclosed inside of a positively charged sphere that makes up an atom.
- The magnitudes of the positive and negative charges are identical to one another. Because of this, the atom as a whole is electrically neutral.
Advantages of Plum Pudding Model
- The benefit is that it is the very simple visual representation of an atom.
- His atomic model comprised of a vast cloud of positive matter with embedded negative particles, resulting in a neutral total mass.
Disadvantages (Limitations) of Plum Pudding Model
It was unable to describe the stability of an atom since his model of an atom was unable to explain how a positively charged electron could be held in an atom by a negatively charged positively charged proton.
As a result, this hypothesis is flawed since it does not take into consideration the location of the nucleus inside an atom.
- The dispersion of alpha particles by thin metal foils was not accounted for in Thomson’s model, which was a failure.
- There is no empirical data to support this theory(model).
- When compared to frequencies released from other substances, this model was unable to explain the emission of an electron spectrum that consisted of various frequencies from Thomson’s atom. These frequencies were emitted from other substances.
- In addition, it was unable to provide an explanation for the existence of the light spectrum.
- In addition, it is unable to provide a mechanism that adequately explains the deflection of the α – particle.
What is the charge of the pudding component?
In Thomson’s atomic model, positive charge is assumed to be spread equally across the volume of the sphere, which is referred to as pudding, while negatively charged particles, i.e., electrons, are assumed to be dispersed as point charges in shells.
What were the reasons for the failure of Thomson’s model of the atom?
The stability of an atom could not be explained using the Thomson model of an atom – i.e., it could not explain how a positively charged portion of the atom could keep the electrons that had a negative charge.
It was unable to provide an explanation for the location of the nucleus inside an atom or for the dispersion of alpha particles.
Replacement of the Plum Pudding Model
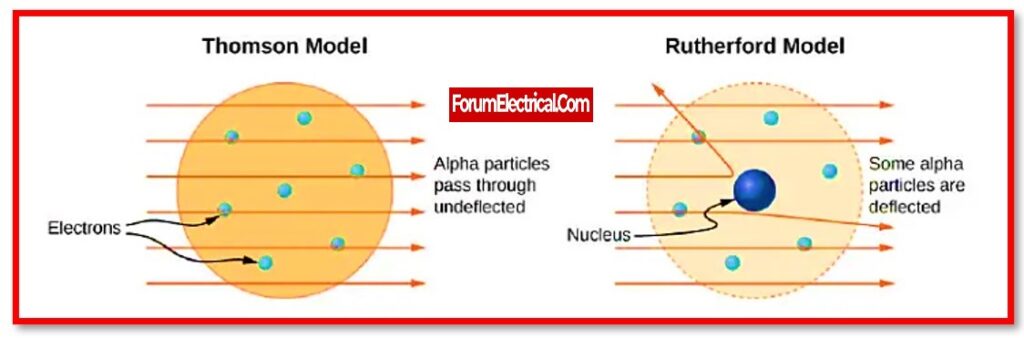
Ernest Rutherford, a British physicist, proposed an atomic model in 1911 that explain the below mentioned phenomena, such as the hydrogen spectrum consisting of the different frequencies, the light spectrum consisting of the different frequencies, and the deflation of α – particles in the external field.
As a result, in 1911, Ernest Rutherford’s nuclear model of the atom supplanted (replaced) Thomson’s Plum Pudding Model.
Why did Rutherford invalidate JJ Thomson’s model?
Thomson’s plum pudding model of the atom had negatively charged electrons inside a positively charged “soup.” The gold foil experiment by Rutherford demonstrated that the atom is essentially empty space with a small, compact, positively charged nucleus.
Rutherford suggested the nuclear model of the atom based on these observations.
Conclusion
Although though Thomson’s model did not provide an accurate representation of the atomic structure, it still provided the basis for the creation of a variety of different models of the atom.
The analysis of the atomic nucleus and the structure of atoms has opened the way for a variety of innovations that have been critically important to the evolution.