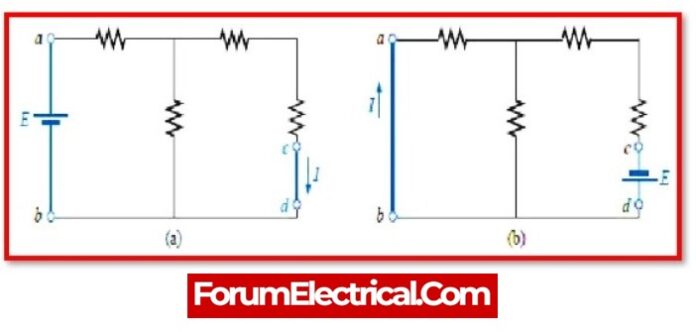
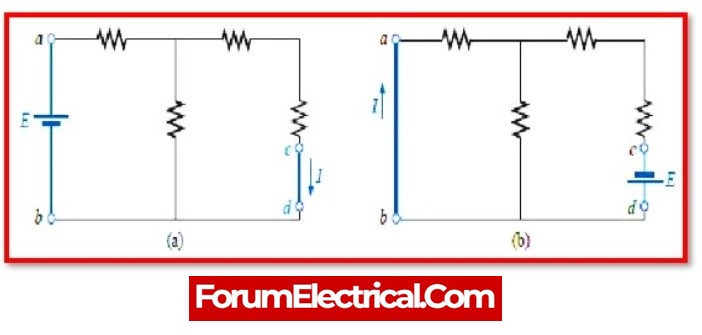
The Reciprocity Theorem is a principle in electromagnetics that relates the voltage and current at two points in a linear, passive network. It states that the ratio of the voltage at one point to the current at another point is equal to the ratio of the current at the first point to the voltage at the second point.
What is the formula for the reciprocity theorem?
Mathematically, the Reciprocity Theorem can be expressed as:
V1/I1 = V2/I2
where:
V1 – the voltage at the first point
I1 – the current at the first point
V2 – the voltage at the second point
I2 – the current at the second point
The Reciprocity Theorem is based on the idea that the relationships between voltage and current in a linear, passive network are reciprocal. This means that the voltage and current at any two points in the network can be interchanged without affecting the overall behavior of the network.
The Reciprocity Theorem is a useful tool for analyzing and designing electrical circuits and systems, particularly when the circuit or system is symmetrical. It allows engineers to use symmetry to simplify the analysis of the circuit or system, making it easier to understand its behavior and to design it effectively.
The Reciprocity Theorem is only applicable to linear, passive networks. It is not applicable to nonlinear networks or to networks with active elements, such as amplifiers.
Where can see the application of the reciprocity theorem?
Reciprocity theorem is utilised in both
- Direct current circuits and
- Alternating current circuits.
The reciprocity theorem, in layman’s terms, asserts that when the locations of the any network’s voltage and current sources are switched, the same or equal amount of voltage and current flowing through the circuit.