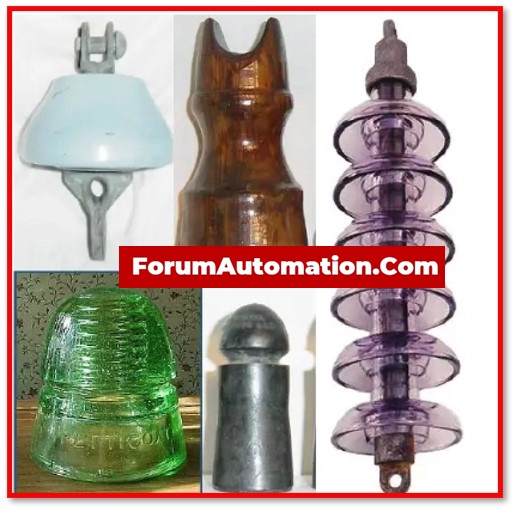
To prevent current flow towards earth, an insulator supports the overhead line (transmission lines) conductors on the poles. It is necessary for the transmission lines to function properly.
To prevent current from flowing to earth, overhead line conductors in transmission line are supported on the poles/turns by insulators.
As a result, the insulator is essential for the effective operation of the lines.

What is the purpose of an insulator?
Insulators are any materials that prevent electrical current from flowing through them.
They serve as a protection mechanism in appliances and electrical circuits found in the house, and they also provide the necessary insulation that is required between the line conductor and the ground.
Insulators are characterised by a high resistance and a low conductivity. Insulators prevent the loss of current and make an electrical current better efficient by regulating the flow of the current.
Insulators also protect against the loss of current.
Function of Insulator
Energy always flows from hot to cold. Heat always moves from hot to cold. Insulation prevents energy transfer from a warmer to a colder object. Insulators block energy transfer.
Particles in motion make up all objects. Bonds connect things. Insulators have strong particle bonds.
Energy transfer is low in insulators because particles move slowly. Particles cannot gain power and raise temperature.
Conductors can quickly transfer energy between particles due to loose connections. Metals conduct effectively.
Importance of Insulators
- Support in the protection of switchgear, transformers, and other substation systems.
- Helps in providing protection from heat, noise, and electric current.
- Probably support the conductor in the overhead line.
- Provide an insulating barrier between the ground and the live portions of the equipment or conductor.
Types of Insulating Material in Transmission Line
An insulator can be designed using a variety of materials such as rubber, wood, plastic, mica, and so on.
- Glass,
- Ceramic,
- PVC,
- Steatite,
- Polymer, and
- Other special materials
are used in the electrical system.
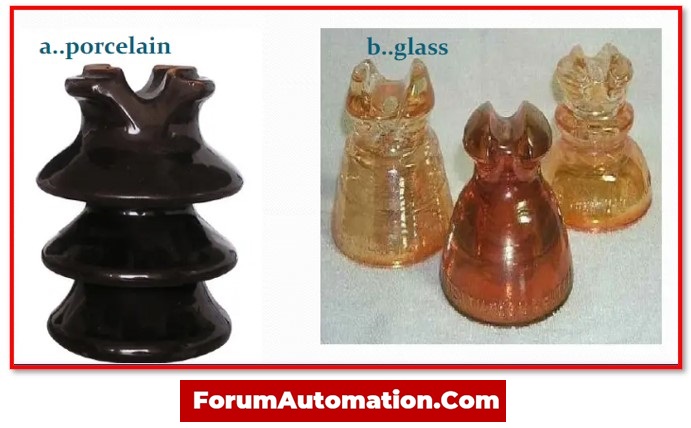

However, porcelain is the most commonly used material in insulators, though special composition, steatite, and glass materials are also used.
Insulator Characteristics
Insulators have unique properties that established them apart from the other electrical devices. Insulators have the following characteristics:
- High resistance.
- Excellent mechanical strength for conductor load.
- The insulator material’s high relative permittivity.
- Excellent dielectric strength.
- Non-porous or waterproof.
Types of Insulators
The following are some of the most common insulators used in power transmission lines:
1). Disc insulators
2). Post insulators
3). Pin insulators
4). Strain insulators
5). Suspension insulators
6). Shackle insulators
7). Stay insulators
8). Polymer insulators
9). Glass insulators
10). Long rod insulators
1). Disc Insulators
The shape of these insulators, which resembles a disc, gives rise to their name. These insulators are used in high-voltage transmission & distribution lines. Disc insulators provide the required electromechanical strength.
Furthermore, they are the low-cost option for polluted areas with medium to low pollution levels.
These insulators, which have the high-efficiency qualities such as reduced corrosion & a strong structure, are used in transmission lines as well as industrial and commercial applications.
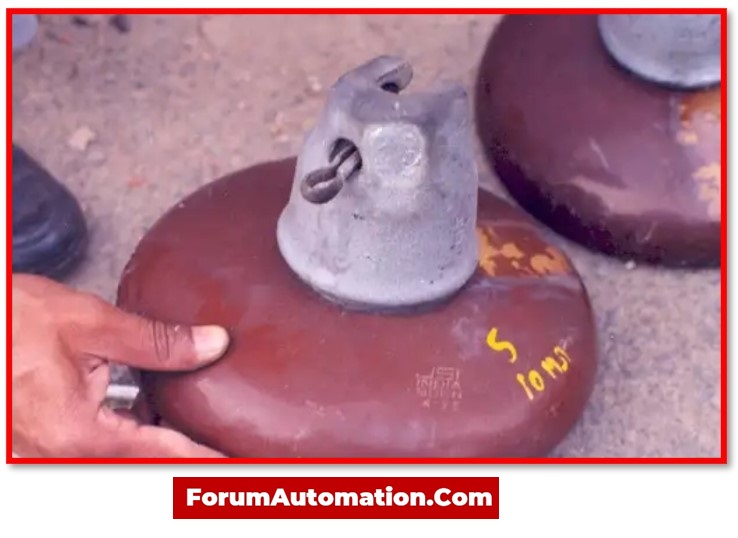

They provide the insulation and also support for line conductors in suspension & tension systems. It can also maintain the high voltages under heavy load.
2). Post Insulators
This particular form of transmission line insulator is the high-voltage insulator that is capable of managing a variety of voltage levels; hence, it is an excellent choice for usage in substations.
They are utilised to ensure that the electricity that is produced in the power plants is delivered in a manner that is both secure and dependable.
Ceramic (or) a single piece of the composite material (silicone rubber) are the two materials that are used to manufacture post insulators, which have the capacity to withstand up to 1100 kV of electricity.
When installed vertically, it is frequently put to use to the protect transformers, switchgear, & other associated pieces of equipment due to the exceptional mechanical capabilities it possesses.
3). Pin Insulators
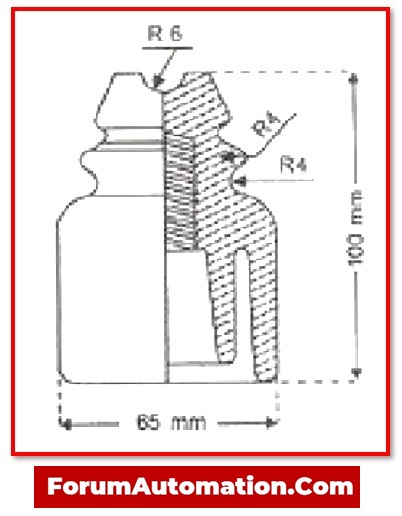
Pin insulators are commonly found in the power distribution lines. It is a device that protects a wire against the physical support, such as the utility pole pin – wooden (or) metal dowel.
It is a non-conducting, single-layer shape made of the porcelain (or) glass.
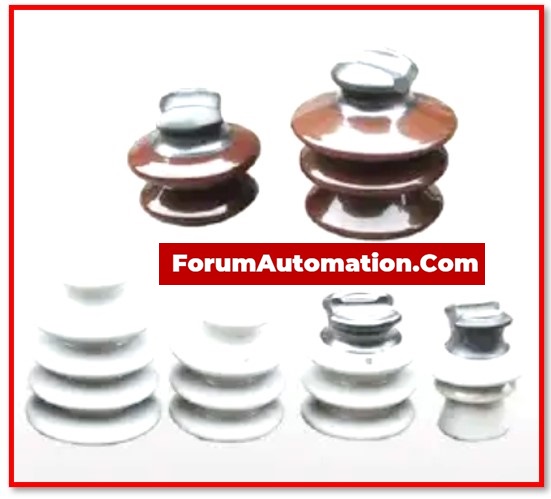

On the physical support, one or more pin insulators may be used depending on the voltage application.
The pin insulator is made of a high mechanical strength material & can withstand voltages of up to 11kV. These can be arranged vertically or horizontally.
4). Strain Insulators
When subjected to the mechanical stress, these insulators are designed to withstand the stretch of the hung electrical wire or cable.
It is similar to the suspension insulator in that it is used to the support radio antennas and overhead power lines.

A strain insulator is used between two lengths of wire to electrically disconnect (unplug) them while maintaining a mechanical connection.
When a wire connects a pole or tower, it can also be used to produce the pull of wire to sustain while electrically insulating it. These insulators have a voltage potential of around 33kV.
5). Suspension Insulators

Insulators similar to this one is typically used in the position of conductors in order to protect overhead transmission cables.
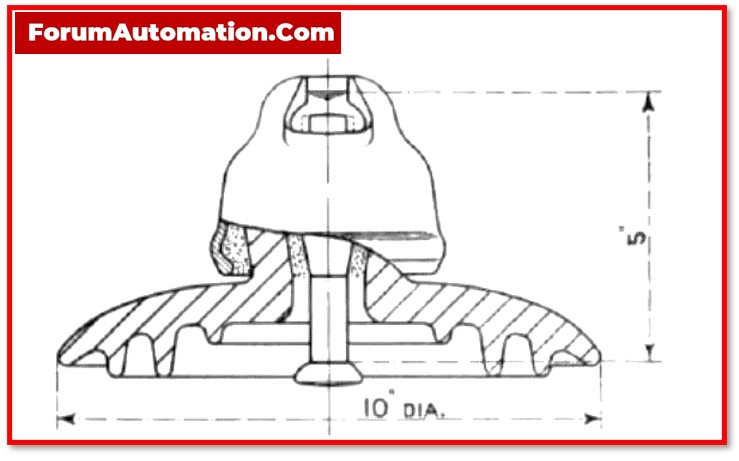
A form of insulator known as the suspension insulator is made of porcelain and found widespread application in the construction of towers.
They make use of a form string that is connected to a series of insulators in succession.

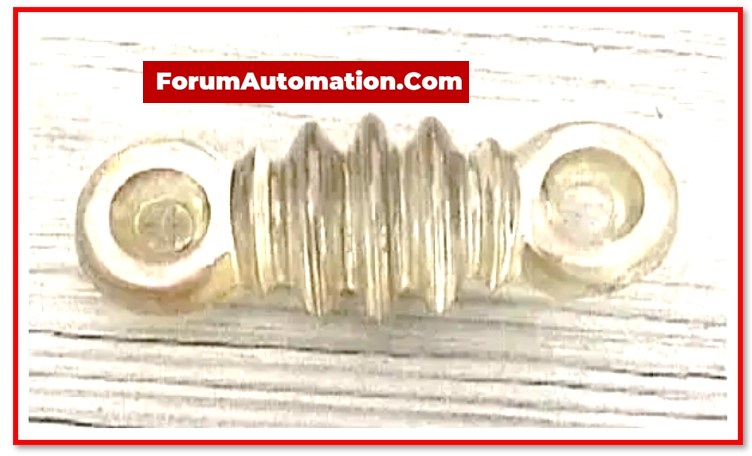
6). Shackle Insulators
Shackle insulators are used in the low voltage distribution systems & are typically very small in size.
This type of insulator is applicable vertically as well as horizontally. This insulator has the voltage carrying capacity of approximately 33 kV and is capable of being connected with a metal strip.

It has the tapered hole that distributes the load force evenly, reducing the risk of the fracture when heavily loaded.
Following the widespread use of the sub-terranean cables for the distribution, the use of insulators has recently declined.
7). Stay Insulators
Stay insulators are the low-voltage insulators that balance & fasten dead-end poles by combining a stay wire & a primary grip.
These rectangular insulators are smaller in size than the other types of insulators.

These insulators can be installed between line conductor & earth. They also serve as the protection devices, guarding against sudden voltage changes caused by faults.
The value of these insulators is obvious when the poles collapse to the ground (or) the stay wires are accidentally damaged due to increased mechanical load.
8). Polymer Insulators
Insulators of this type are the electrical devices that are usually made of the polymer materials and have metal fittings.
Moreover, these insulators are made of fibreglass rods and are surrounded by polymer weather shelters. Weather shades shield the insulator core from the elements.
Polymer insulators are the lighter and more powerful than porcelain insulators. It is widely regarded as a good heat & electrical insulator.
It is used as an insulator due to its unconventional electrical, mechanical, chemical, & thermal properties.
9). Glass Insulators
Insulators of this type are made of the annealed (or) toughened glass and are used in the power transmission lines.
It is the property of this insulator to insulate electrical lines so that the electricity does not leak into the poles & the ground.
Glass insulators were once used in telegraph & telephone lines.
Toughened glass types were developed to counteract the fragility of glass, and they quickly gained popularity due to their longer lifespan.
10). Long rod Insulators
Long rod insulators are the commonly hinged on the steel towers to insulate transmission lines.
Furthermore, by properly supplying power, they serve as the safety devices.
Long rod insulators are typically composed of several insulators, depending on usage and demand.
These are the porcelain rods with the weather sheds & metal end fittings on the outside.
This insulator has the advantage being suitable for both tension & suspension applications.
Applications of the Insulators
The applications are as follows:
- These are used to ensure safety techniques in circuits and electric boards.
- Insulators shield materials from the electricity and heat.
- Daily products are made from plastics and rubbers.
What is meant by insulation breakdown?
Insulation breakdown occurs when the breakdown voltage is applied to an insulator, causing it to become conductive.
Conclusion
An insulator is a type of equipment that cannot effectively conduct electricity.
As a result, a clear overview of the insulators used in the transmission lines can be obtained, with each type serving a specific purpose.
When choosing an insulator, several factors must be considered, including its dielectric element, operating temperature, economic factor, and recognised substance.









