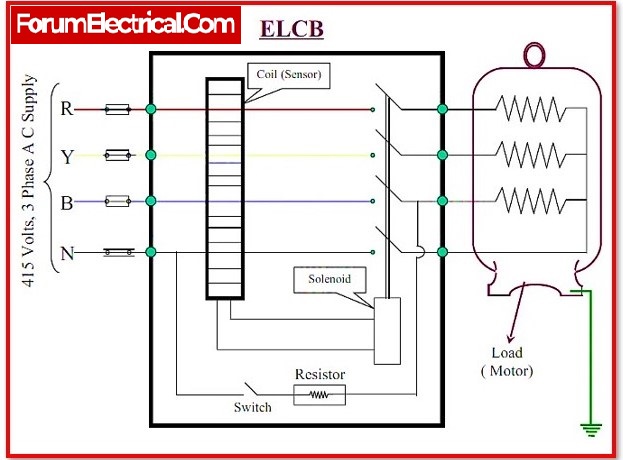
- What is meant by Earth Leakage?
- What Causes Earth Leakage?
- What is ELCB?
- Function of the ELCB
- Operation of the ELCB
- How to Install an Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker?
- Advantages of ELCB
- Disadvantages of ELCB
- Applications for ELCB
- Types of the ELCB
- Based on their operation
- 1). Voltage Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker
- 2). Current Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker
- Based on the poles
- 1). 2-Pole ELCB
- 2). 3-Pole ELCB
- 3). 4-Pole ELCB
- How to Check an Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker?
- Difference Between ECLB and MCB
- ECLB VS MCB
- What are some ways to reduce the earth’s leakage current?
- What Causes Leakage Current in a Circuit?
- ELCB Codes & Standards
- Why is ELCB important for Electrical Safety?
- What is the purpose of ELCB?
What is meant by Earth Leakage?
Earth leakage is the transfer of electrical current from a live conductor to the earth via an unintentional path. It may pass between their inadequate insulation or through a person’s body, resulting in electrical shock. If the leakage current surpasses 30mA, the result of an electrical shock can be lethal. When such current leakage is detected, protection devices are utilised to disconnect the power source.
What Causes Earth Leakage?
Earth leakage can occur for a wide range of causes.
- It might happen owing to faulty live conductor insulation or broken conductors.
- It can also happen if the live conductor comes into touch with the body of the device and it isn’t properly grounded.
- The current can travel through the person’s body when they touch the conductor or the equipment.
What is ELCB?
ELCB – Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker
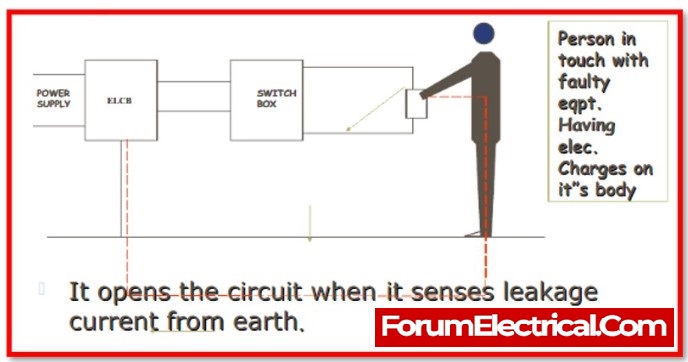
An earth leaking circuit breaker is a safety device used in both residential and commercial electrical circuits with high earth impedance to prevent electric shocks. It detects minor stray voltages on electrical equipment’s metal casings and cuts the circuit if a harmful voltage is detected.
ELCB’s help in the detection of current leakage and insulation failures in electrical circuits, which could result in electrical shocks to anyone in contact with the circuit.

ELCB’s are primarily used to protect against electrical shock. They do not provide overload or short circuit protection. As a result, they must be used in conjunction with an MCB-miniature circuit breaker.
Function of the ELCB
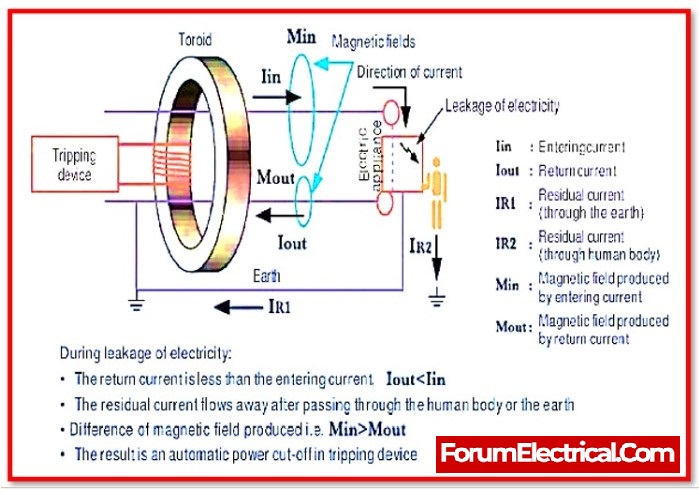
Because it is a safety device, the main function of an earth-leakage circuit breaker, or ELCB, is to prevent shock when electrical installations through high Earth impedance. This circuit breaker detects minuscule stray voltages on top of electrical devices using a metal shell and interrupts the circuit if a hazardous voltage is detected. The primary function of ELCBs is to prevent electric shock from causing injury to humans and animals.
Operation of the ELCB
An electrical circuit breaker is a type of latching relay that has a mains supply of buildings connected through its switching contacts so that when earth leakage is detected, the circuit breaker will disconnect the power. The fault current from live to the ground wire in the fitting it protects can be identified using it. If sufficient voltage is applied across the sensor coil of the circuit breaker, it will shut off and remain off until physically reset. An ELCB utilised for voltage sensing cannot identify fault currents.
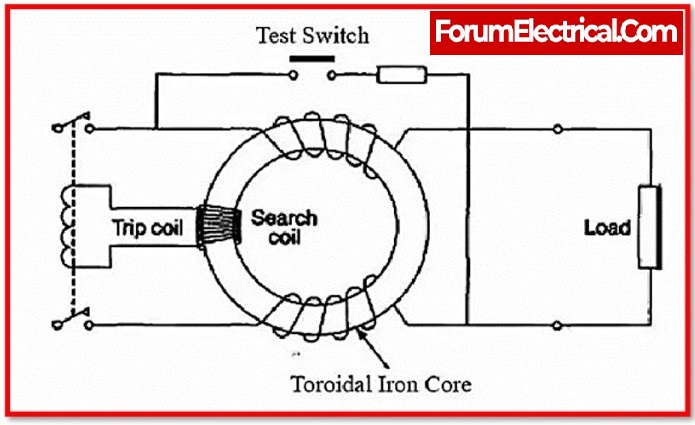
How to Install an Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker?
When an ELCB is employed, the earth circuit is modified; the connection to the earth rod is recognized through the earth leakage circuit breaker by connecting to its two earth terminals. One connects to the appropriate earth circuit protecting conductor (CPC), and the other to an earth rod or similar type of earth connection. As a result, the earth circuit allows current to flow through the ELCB’s sense coil.
Advantages of ELCB
- To avoid electrical shock, the ELCB immediately breaks the circuit.
- It protects against harm caused by broken wires (or) damaged insulation.
- The ELCB is not a device that is easily affected by faults.
- It is also economical in addition to being effective.
- In this operation, once the installation of ELCB has two connections toward the earth (ground), high-current lightning that is close to the ground will strike to cause a voltage gradient within the soil. As a result of this voltage gradient, the ELCB will be able to sense the coil by a sufficient voltage to cause it to safely trip.
Disadvantages of ELCB
- Overloading and short circuit current are not protected by ELCB.
- It is incapable of protecting against live-neutral shock.
- It may trip unnecessarily as a result of minor current leaks in obsolete equipment.
- The load protection provided by ELCB requires the usage of a reliable earth connection.
- If the earth rod is near another building ground, a current with high earth leakage from many other constructions might increase the potential of earth to generate a voltage differential across the earth to trip the ELCB again.
Applications for ELCB
- ELCBs are used to prevent current leakage.
- Electrical shock and system problems are caused by current leakage.
- It instantly breaks the circuit to prevent damage to the associated circuits.
- They are needed in moist areas where electrical shocks are more likely.
Types of the ELCB
Based on their operation
ELCBs are categorised into two types based on their operation principle:
- Voltage Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker and
- Current Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker
Both types of ELCBs detect leakage current, but their sensitivity and level of protection differ. The current ELCB was invented before the voltage ELCB. Voltage-based ELCBs are inferior than current-based ELCBs. To minimise uncertainty, the voltage ELCB has been renamed ELCB, while the current ELCB has been called RCCB or RCD.
1). Voltage Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker
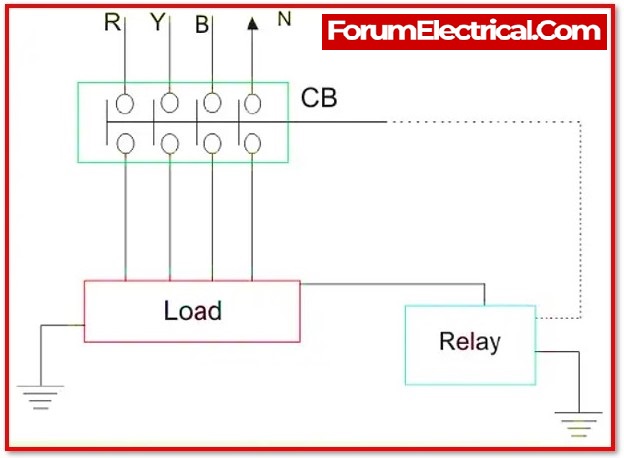
Voltage ELCB function on the voltage level between the earth and the equipment’s body. The voltage difference is utilised to identify leakage current and break the circuit immediately.
It contains terminals for both phases and neutral on both the supply and load sides.It contains two additional terminals that link to the body of the equipment and the ground. These terminals are linked to the electromagnetic relay and play an important function in breaking the circuit during current leakage.
Working Principle of Voltage ELCB
One terminal of the relay coil is directly connected to the earth, while the other is attached to the equipment’s body. The coil senses the voltage difference between the earth and the body of the equipment.
A voltage difference arises across the terminals of the coil if the live wire breaks or its insulation fails and comes into touch with the body of the apparatus. As a result, current begins to flow through the coil, and it becomes activated. The relay begins to produce electromagnetic force. When the current surpasses a specific threshold, the relay generates enough force to lift the latch. The latch break then opens the connections, disconnecting the power supply to the machine and preventing electrical shock.
As a result, the earth connection is required since the relay activates only when the leakage current runs through it. If the current leaks through any other portions of the circuit and flows through any other undesired path, the circuit will not be broken since the current must flow through the relay in order for the circuit to be broken.
Advantages of Voltage ELCB
- It helps in the prevention of electrical shocks.
- They are less sensitive and do not trip as often.
- They are less costly.
Disadvantages of Voltage ELCB
- It is unable to detect current leakage from the phase to any other earthed body.
- It cannot protect against electrical shock if the phase conductor is physically touched.
- Only when the leaking current travels through the ground conductor does it trip.
- It requires an additional connection with the equipment’s body and the soil.
- It has a lower sensitivity and cannot detect minor leakage current.
- Electrical equipment that usually leaks voltage may cause the ELCB to trip unnecessarily.
Applications of Voltage ELCB
- The voltage-operated E.L.C.B. is typically utilised in locations that have poor earthing conditions such as rocky or dry sub-soil.
2). Current Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker
Current ELCBs, also known as RCDs (Residual Current Devices) or RCCBs (Residual Current Circuit Breakers), are another type of ELCB that breaks the circuit when a leakage current is detected. It works by measuring the current difference between the phase and neutral lines. When current leaks from the phase line, the difference occurs. As a result, RCCBs can protect against any type of current leakage.

It has four terminals, two input and two output for phase and neutral. The phase-in and neutral-in connections are connected to the supply, while the phase-out and neutral-out connections are connected to the load. It lacks the extra terminal for earth connection.
Working Principle of Current ELCB
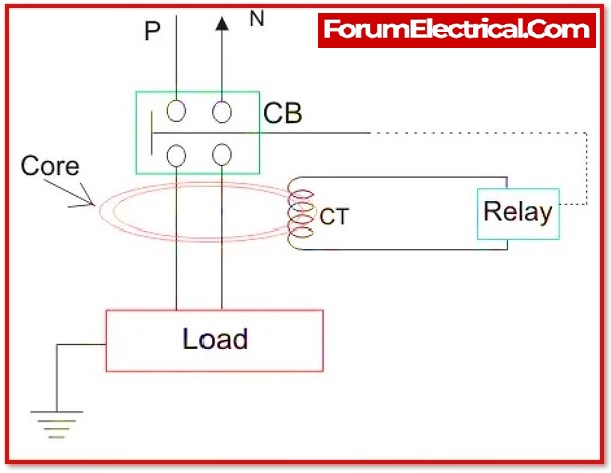
The current operation of an ELCB or RCCB is dependent on the current imbalance between the phase and neutral lines. It constantly measures the phase and neutral currents. Because it is the same current coming back from the load, both phase and neutral current are identical under normal conditions. If the current leaks through an undesired path, it diminishes the neutral current and generates an imbalance. When the imbalance surpasses a particular threshold, the RCCB breaks the connections and cuts off the electricity.
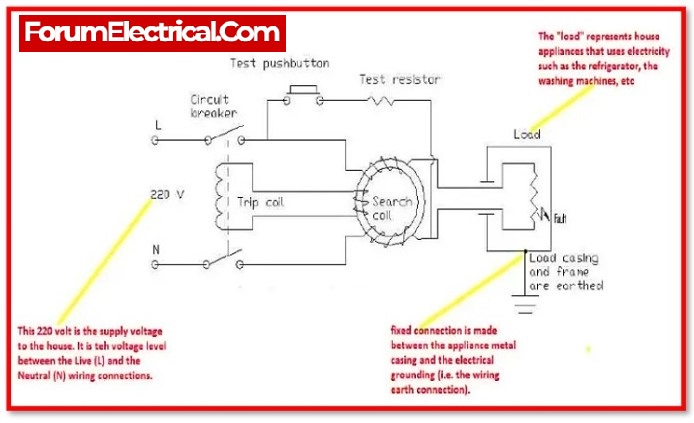
The RCCB operates on the Kirchhoff’s current law principle, which states that the amount of current entering the load through the hot wire should match the amount of current exiting the load through the neutral wire. The residual current should be equal to the difference between the two currents. If there is a discrepancy, it indicates that current is seeping someplace, causing the imbalance.
The RCCB contains a zero-sequence current transformer with three coils: phase coil, neutral coil, and search coil. It detects the imbalance or difference between two currents. The phase coil and neutral coil are twisted around the toroidal core in such a way that their flux cancels out.
If the currents are equal, as they should be under normal conditions, the resulting flux will cancel out and no induced current will be present in the search coil. If there is a leakage current, the difference in current will cause flux, which will induce a voltage in the search coil. Because the search coil is linked to the relay trip mechanism, it will break the connections and cut power to the load.
Advantages of Current ELCB or RCCB
- When current leaks from any section of the circuit, the RCCB breaks the circuit.
- It is quite dependable in terms of delivering electrical shock protection.
- It has a far higher sensitivity than a voltage ELCB.
- It continuously monitors residual current and breaks instantly when it exceeds its rated limit.
- There is no need for an earth connection.
Disadvantages of Current ELCB or RCCB
- It does not give short-circuit current protection.
- It has no overload protection.
- It costs more than ELCB.
- It cannot protect against electrical shock caused by touching both phases and neutral wires since the current remains constant.
- It may trip unintentionally due to its high sensitivity when utilised with old appliances that have minimal current leakage.
- It can only function on standard supply waveforms and cannot operate reliably on the on-standard waveforms.
Applications of Current ELCB
- The current operated ELCB is a prominent type of circuit breaker that is utilised in a variety of commercial, industrial, and residential applications.
Based on the poles
The ELCB is divided into three categories based on the poles of the circuit breakers:
- 2-Pole ELCB,
- 3-Pole ELCB and
- 4-Pole ELCB
1). 2-Pole ELCB
In order to provide protection for a single-phase system, a 2-Pole ELCB is used. It has two terminals that are two ingoing terminal and two that are outgoing terminal, and both of them have phase and neutral connections.
2). 3-Pole ELCB
In a three-wire three-phase system, a 3-Pole ELCB is utilised for the purpose of providing protection. It has three terminals that are three ingoing terminal and three terminals that outgoing.
3). 4-Pole ELCB
In a four-wire, three-phase system, the 4-Pole ELCB serves the function of providing protection.
How to Check an Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker?
The earth leakage circuit breaker should be checked once a year to ensure that it is in good operating condition. Normally, the circuit breakers (CB) are in the ON position.
The procedure for testing the earth leakage circuit breaker is detailed below:
- If the ELCB’s are not working properly, should contact sales or service engineers in the locality.
- To deactivate the breaker, simply push the operation switch so that the power supply is turned off.
- Using a pointed object like a ballpoint pen, press the test button on the earth leakage circuit breaker.
- Verify whether the ELCB is in turned OFF position.
- Return the ELCB to the ON position.
- Switch ON the power supply.
Difference Between ECLB and MCB
MCB, the advanced fuse, breaks circuit contact with supply when current supply exceeds Molded Case Circuit Breaker’s rated current. MCBs break contacts to prevent circuit faults.
Earth Leakage Circuit Breakers can break circuit contacts via the mains supply like Molded Case Circuit Breakers. It doesn’t break circuit contacts if supply current unexpectedly increases, unlike the MCB. When a circuit operation shocks someone, this circuit breaker cuts the current.
ECLB VS MCB
| S.NO | ELCB | MCB |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ELCB is the abbreviation for an Electric Leakage Circuit Breaker. | Molded Case Circuit Breaker is the abbreviation for the MCB. |
| 2 | An ELCB is a voltage-controlled earth leakage device. | The MCB is a type of electromechanical device. |
| 3 | ELCB are advanced, and they respond quickly when a circuit leaks the current to earth. | MCB is a basic protection device that is used to limit current and fault inside a circuit. |
| 4 | The earth leakage circuit breaker is based on the principle of current balancing. This implies that it points out the total amount of incoming and outgoing current. | According to the MCB principle, which works on the incoming current measurement and increase for the circuit. |
| 5 | ELCBs are instant type because they must respond instantly to any earth fault. | MCBs are classified according to their application and characteristics. |
| 6 | As a result, with different MCB resets, it is optional to properly examine the circuit before resetting ELCB. | In comparison to the MCB, the trip ELCB describes a more alarming problem (fault) in the circuit. |
| 7 | The rated current of an ELCB can range anywhere from 5 to 50A operating at 240VAC. | The rated current of the MCB is not greater than 125 A. |
What are some ways to reduce the earth’s leakage current?
Using a 4-conductor filter with a neutral conductor rather than a 3-conductor filter is an approach that is both particularly easy and highly efficient for lowering the amount of leakage current.
What Causes Leakage Current in a Circuit?
Leakage current is caused by the unintended flow of current through an insulating material, such as a capacitor or insulation, in an electrical circuit. It can be caused by several factors, including material impurities, defects in the insulation, temperature changes, and electrical stress. The presence of leakage current can result in power loss and potentially cause damage to the circuit over time.
ELCB Codes & Standards
IEC 61008-1: The International Electro-technical Commission (IEC) has developed a complete standard for Residual Current Operated Circuit Breakers (RCCBs) without integral overcurrent protection for domestic and similar applications, which includes ELCBs.
EN 61008-1: the European equivalent of IEC 61008-1, specifies testing procedures and criteria for ELCBs within the European Union.
BS 7671: British Standards BS 7671, often known as the IET Wiring Regulations, specifies installation and safety criteria for electrical installations in the UK, including ELCBs.
NFPA 70 (NEC): The National Electrical Code (NEC) of the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) in the United States includes rules for the usage and installation of Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCIs), which are analogous to ELCBs.
IS 12640: IS 12640 by the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) outlines ELCB construction, performance, and testing requirements.
Why is ELCB important for Electrical Safety?
Electrical safety must always be the primary priority, whether in a residential or commercial situation. The ELCB is an important device for preventing electrical shocks and fires. Learning what an ELCB is & how it operates can literally save lives. An ELCB, which is additionally recognized as an Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker (or) ELCB circuit breaker, is a safety device that measures the electrical current that flows through a circuit. It automatically disconnects the power supply if it detects even a minor leakage of electricity to earth, preventing electrocution or electrical fires.
What is the purpose of ELCB?
The principal function of an Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker (ELCB) is to prevent electric shocks & electrical fires occurred by ground faults (or) leakage currents. An ELCB fulfills the following purposes:
- Personal Safety
- Fire Prevention
- Equipment Protection
- Compliance with Safety Regulations
Personal Safety
ELCBs are intended to detect any current leakage to the ground, which might occur due to poor insulation, damaged wiring, (or) contact with conductive surfaces. When a leakage current exceeds a predefined safe threshold, the ELCB trips and disconnects the power supply, preventing potentially lethal electric shocks to persons.
Fire Prevention
In the case of a ground fault (or) leakage current, electricity may seek an alternate path through flammable materials, resulting in overheating and hazardous electrical fires. ELCBs serve to reduce the risk of fires caused by leakage currents by disconnecting the power supply quickly.
Equipment Protection
Leakage currents can cause long-term harm to electrical equipments. ELCBs help protect these devices by cutting off the power supply if a leakage current is detected, limiting additional damage or failures.
Compliance with Safety Regulations
To maintain a safe & reliable electrical system, many countries and areas require the installation of ELCBs, especially in residential, commercial, & industrial environments.