- What is Megger?
- What is Megger test?
- Why is Megger Testing Performed?
- What is done during the Megger testing?
- How Does Megger Testing Work?
- Megger Test Working Principle
- Advantages of Megger Testing
- Types of Megger Test
- Advantages of the Electronic Type Megger Test
- Advantages of the Hand Operated Megger Test
- Precautions for Megger Testing
- Megger Testing
What is Megger?
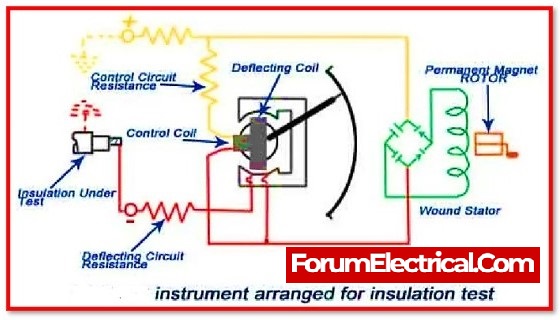
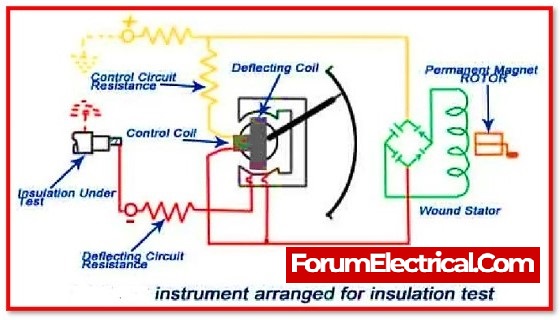
The Megger is the instrument that is used for the purpose of measuring the insulation’s resistance.
The resistance of the insulation is compared with a value of resistance that is previously known, which is how it functions on the basis of the principle of comparison.

If the resistance of the insulation is high, the pointer of the moving coil will deflect towards infinity; however, if the resistance of the insulation is low, the pointer will show that there is no resistance.
When compared to other types of equipment, the Megger has a high degree of accuracy.
What is Megger test?
The Megger test is a method of testing that uses an insulation tester resistance metre to verify the state of electrical insulation.
An electrical wire is made up of a conductor and an insulator. The interior metal strap in a wire is the conductor, while the outer rubber coating covering the conductor is the insulation.
Users are able to touch the live wire because of the insulation (not the metal strap).
Insulation is a type of resistance measurement. The higher the resistance, the better the insulation.
The quality of an electrical system’s insulation resistance declines with time and environmental conditions such as
- Temperature,
- Humidity,
- Moisture, and
- Dust particles.
It is also severely impacted by the presence of electrical and mechanical stress, so it is important to monitor the IR (Insulation resistance) of equipment at regular intervals to avoid any measure lethal (fatal) or electrical shock.
The IR measures an insulator’s ability to withstand a service voltage without a current leakage path. It indicates the state of an insulator.
It is tested with a Megger test, which can induce D.C. voltage between its two probes while automatically computing and displays the IR value.
Why is Megger Testing Performed?
Megger Test” is to ensure the integrity of the wiring system.
When there is a fire or another high heat event (explosion), the wiring and its corresponding elements like insulation are subjected to extreme heat.
Melting points exist for all metals and physical substances.
During some fires, this melting threshold is reached, affecting the wiring’s current carrying integrity. The insulation might have melted inside, or both the wire and the insulation could have melted.
When this occurs, an area of resistance arises as the electrical current attempts to flow through the melted area.
Heat is produced as current flow increases in an effort to travel the area. That heat could generate enough heat to start another fire.
The scary part about these damaged cables is that users may not be aware of it because the wire is damaged behind the walls.
Megger testing causes no damage, making it a good option when no holes in walls are available to test electrical insulation for faults or abnormalities.
The testing instrument only operates at a relatively modest voltage range of 500 to 1,000 volts.
Because of the low voltage, some insulation punctures remain undetected. It normally provides information on leakage current, if insulation areas have
- Excessive dirt or moisture,
- Quantity of moisture,
- Degradation, and
- Winding problems.
What is done during the Megger testing?
It is necessary to test the circuits to determine whether there is any melted fault areas or existing connections that may have been damaged by the fire.
After that data have been analysed, individual circuits can be identified and replaced in order to ensure that there will be no more issues with the circuits that have been damaged.
How Does Megger Testing Work?
In some cases, a multimeter is utilised as an insulation tester, and just a continuity test is conducted. However, a particular device known as an Insulation tester is used to identify and test for a leakage current during a normal or overloaded situation.
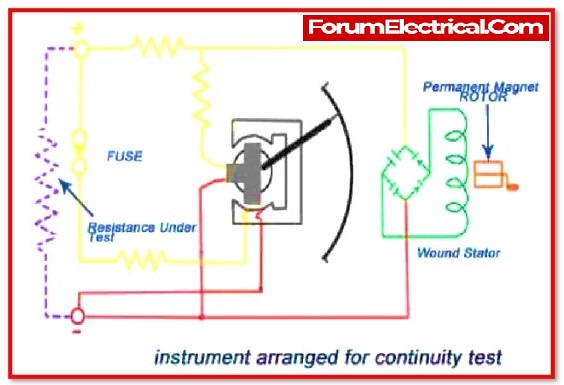
It is necessary to measure electrical leakage in wires and get extremely dependable results because it will be flowing electric current through the equipment while testing.
Users test the electrical insulation of any equipment, including a motor, wire, generator winding, or general electrical installation.
This is a common test that has been used for a long time. It does not included in the specific location of the electrical puncture, but it does show the quantity of leakage current and the level of moisture within the electrical equipment or winding or system.
The following is the procedure for performing an insulating resistance test or a megger test:
First, users will disconnect the transformer’s line and neutral terminals.
Megger test leads are attached to the LV and HV bushing studs to measure the Insulation Resistance IR value between the LV and HV windings.
Megger test leads are attached to HV bushing studs and the transformer tank earth point in order to measure the Insulation Resistance IR value between the HV windings and the earth.
Megger test leads are attached to LV bushing studs and the transformer tank earth point in order to measure the Insulation Resistance IR value between the LV windings and the earth.
The empirical relationship shown below yields the suggested minimum value for IR in mega ohms (MΩ).
The value measures the insulation strength of the cable and whether or not it has deteriorated.
IRmin (in MΩ) = kV + 1
Where kV = rated service voltage (KV).
Megger Test Working Principle
- Voltage for testing produced by hand operated megger test by crank rotation in case of hand operated type, an electronic tester is powered by a battery.
- 500 volts direct current is recommended for testing equipment with a voltage range of up to 440 volts.
- High voltage electrical systems are tested with voltages ranging from 1000 V to 5000 V.
- The deflecting coil or current coil is connected in series and permits the electric current taken by the circuit to flow.
- The pressure coil, also known as the control coil, is linked across the circuit.
- Current limiting resistors (CCR and PCR) are connected in series with the control and deflection coils to prevent against damage in the event of extremely low resistance in the external circuit.
- The electromagnetic induction effect is utilised to produce the test voltage in hand operated megger tests, i.e., the armature is arranged to move in a permanent magnetic field or vice versa.
- In comparison, an electronic type megger test battery is utilised to generate the testing voltage.
- The deflection of the pointer grows as the voltage in the external circuit increases, and lowers as the current increases.
- As a result, the resulting torque is proportional to voltage and inversely proportional to current.
- When the electrical circuit being tested is open, the torque due to the voltage coil is at its maximum, and the pointer reads ‘infinity,’ indicating that there is no shorting across the circuit and maximum resistance within the circuit under test.
- If there is a short circuit, the pointer displays ‘zero,’ indicating that there is no resistance within the circuit being checked.
Advantages of Megger Testing
- Proactive Technology Condition Evaluation
- Reduced Emergency Risk Failure of the Power System
- Guaranteed Availability
- Predictive Maintenance
- Asset Administration
- Predictive Technology Average Life Expectancy
Types of Megger Test
This can be divided into two categories:
- Electronic Type – Battery Operated
- Manual Type – Hand Operated
Advantages of the Electronic Type Megger Test
- A very high level of accuracy can be expected.
- The IR value is displayed in digital format and is simple to understand.
- The operation can be done relatively effortlessly by one person.
- Even in extremely crowded conditions, it functions without a hitch.
- Very convenient and risk-free to use.
Advantages of the Hand Operated Megger Test
- Due to the fact that it is one of the oldest methods for determining an IR value, still it maintains its significance in today’s highly technological environment.
- There is no requirement for any external source in order to run.
- Cheaper accessible in market.
Precautions for Megger Testing
- If the following minimum safety precautions are not followed while using a megger test, users could get harmed or damage the equipment.
- Only use the megger test for high-resistance measures, such as insulation testing or checking two distinct conductors on a cable.
- Never touch the test leads while cranking the handle.
- Before connecting a megger test, de-energize and discharge the circuit completely.
- Before using a megger test, disconnect the device being tested from another circuitry if possible.
Megger Testing
Megger testing is a technique for measuring the insulating resistance of electrical systems & equipment. It facilitates in the detection of faults, degradation, (or) moisture that may impact insulation, assuring safety and preventing malfunctions in electrical systems.