Excel Calculator
The Reactive Power Calculator Excel Tool simplifies AC circuit analysis by precisely calculating reactive power.
In electrical systems, reactive power is the power that oscillates between source & load due to inductive (or) capacitive elements and is important.
Reactive power is easily determined with our tool, helping electrical systems be optimized and troubleshot. Users can calculate reactive power quickly by entering current power factor, required power factor and actual power (P).
It’s easy to comprehend AC circuit power dynamics using this Excel tool for electrical engineers, technicians, and students. Use our Reactive Power Calculator Excel Tool for better evaluation and selection.
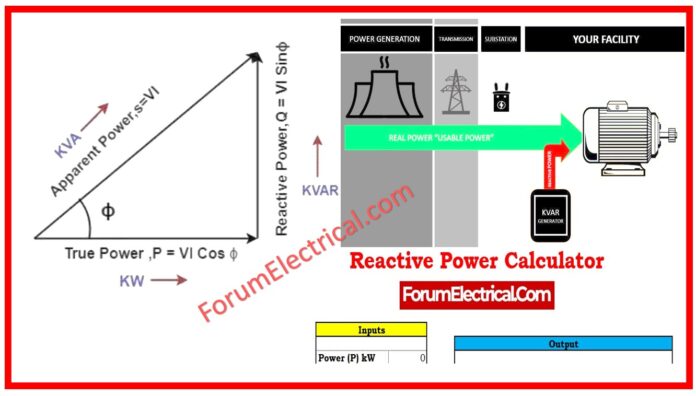
What is KVAR?
KVAR units or energy savings devices is to reduce energy expenditures. These units reduce utility bills, especially for AC systems, in homes and industries.
Three terms describe alternating AC power.
- The first is the true power kilowatt. This is how utility meters by your house measure power
- KVAR, or Kilovolt-Ampere Reactive, measures reactive power
- Power Factor
Kilovolt-Ampere Reactive measures reactive power in electric power transmission and distribution.
KVAR doesn’t appear on utility meters because you don’t pay for it. KVA or perceived power is the third term. The power factor-the ratio of visible power to active power-will help you understand these ideas.
Active and reactive power make up apparent power.
Lower reactive power components increase power factor and cost savings.
How is KVAR Calculated?
There are numerous techniques to compute a load’s reactive power using KVAR. Use a voltmeter and ammeter (or) amp meter for an accurate method.
Producting the measurements gives the load’s perceived power in volt-amperes.
The value can additionally assist you calculate the load’s watts. With those data, calculating the vectorial difference would appear easy. After calculating reactive power, you can identify capacitors to lower apparent electrical components in those systems.
So you can reduce power factor and save money.
Ex: 30 KVAR of capacitors will lower the utility company’s reactive power to 30 KVAR. However, the utility’s apparent power will reduce to 85.4 kVA.
Reactive Power/KVAR Formula
The unused power created by reactive components in an AC circuit (or) system is measured in KVAR.
Greater reactive power equals higher perceived power (kVA) in power factor. Residential houses utilize few kWhs.
Therefore, firms don’t charge residential premises. Low power doesn’t worry electricity corporations. Electricity suppliers charge commercial and industrial organizations a premium because they use so much.
Formula for KVAR: Required Capacity of kVAr = P (Tan θ1 – Tan θ2)
Where
P – Power in KW
θ1 – Current Power Factor
θ2 – Required Power Factor
To comprehend reactive power, you must understand the formula.
Solved Example
A motor delivers a load of 700 kW with a power factor of 0.65. What capacitor size in kVAr is required to get the P.F (Power Factor) to unity (1)?
Supplying kW = 700 kW.
Current P.F = Cosθ1 = 0.65.
Required P.F = cosθ2 = 1
θ1 = Cos-1 = (0.65) = 49°.45;
Tan θ1 = Tan (41.24) = 1.169.
θ2 = Cos-1 = (1) = 0°;
Tan θ2 = Tan (0°) = 0.
Required Capacitor kVAr to enhance P.F from 0.65 to 1
The required capacitor (kVAr) is calculated as P (Tan θ1 – Tan θ2).
= 700kW (1.169- 0)
= 818.3 kVAr
Click here for more Electrical Calculators