Probes for Electronic Measurement
1). Current Detectors (Current Probes)
Current probes are one of the most important equipment used by electrical engineers to collect measurements when normal clamp-on probes cannot reach.
Tight breaker panels wrapped around odd forms and huge buss bars are examples.
This sensor is very versatile, with an output that may send direct measurements to loggers, power quality devices, DMMs, and oscilloscopes.
In the past, a phase tester was also used to detect the live wire in an alternating current system.
2). Voltage Testers (Voltage Probes)
They are often used to measure high-speed signals with voltages up to 12 volts.
They are ideally suited for measurements on high-frequency circuit components that need the least probe loading.
At high frequencies, a probe with a smaller input capacity may allow for a larger input impedance.
Voltage meters
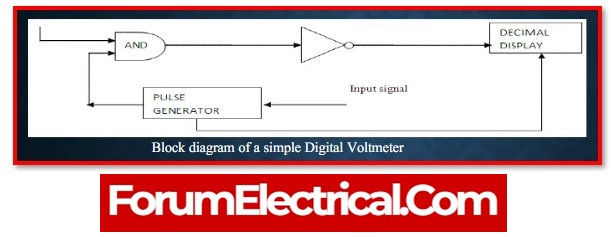
1). DVM – Digital Voltmeter
DVMs are generic devices for electrical engineers which are employed in labs and in the field to measure voltage.
These are the most often used instruments because they show voltage on LEDs (or) LCDs in a manner that electrical engineers can understand.

2). Voltage Analysers (Voltage Testers)
A voltage tester is used to test the existence of voltage in a circuit, as the name implies.
A voltage tester is comprised of a neon bulb with two wires linked to the bottom. This is used to test the current flow in a wire.
A suitable voltage testers (rated up to 500 V), and phase testers were also used for this purpose in the earlier.
Signal Generators
1). Function Generators
A function generator is a kind of testing equipment (or) software that is used to create various types of waves in various shapes and frequencies.
The most frequent wave types are sine, square, and triangle. The function generator generates these forms when mending (repairing) electrical equipment.
While testing both circuits and boards, it is sometimes necessary to have a controlled signal in order to replicate normal functioning.
2). Radio Frequency (RF)
This is the rate of variation in a certain range that receives and responds to radio wave frequency and alternative currents that convey radio signals.
RF currents often do not flow to depth but instead persist at the current’s surface.
Electrical Testers
1). Battery Testers (Battery Examiners)
A battery tester is required for many tasks for electrical engineers.
This is a sort of electrical equipment designed for the purpose of evaluating the status of a battery.
Most tests look for chargers inside the battery’s cells as well as overall voltage output.
Many will actually evaluate the battery’s condition, such as its capacity to acquire a charge and any defects that may have a negative influence on its overall performance.
2). Continuity Testers (Continuity Analysers)
For electrical tools & equipment, continuity testers are common & necessary.
These instruments are used to assess if an electrical channel can be constructed between two points A and B.
These testers help the engineer in assessing whether or not an electrical circuit can be established.
3). Multimeters
A multimeter is a kind of electronic equipment used to measure electrical voltage, current, and resistance.
A “VOM Meter” is another name for this kind of device. This electrical tool can be used to diagnose electrical problems in equipment, motor controls, appliances, wiring systems, and even power sources.
4). Outlet Testers (or) Receptacle Tester
This sort of testing equipment is utilised in a variety of electrical engineering professions.
Although it is most usually referred to as a “Outlet Tester”, it may also be called to as a “Receptacle Tester”.
This instrument is used to evaluate whether a wall outlet that operates and/or distributes AC electricity is properly connected.
Moreover, it may assess whether or not the outlet being checked has power in general.
Wire Tracer
A wire tracer is a type of testing instrument that can identify whether a given set-up has a wire (or) cable that is unshielded (or) de-energized.
This may be done by tracing the path of the wire (or) cable.
Frequency Counter
The measurement of frequency may be done using an electronic equipment known as a frequency counter, or with a component of such an instrument.
In most applications, frequency counters are used to determine the number of oscillation cycles or pulses that occur in one second inside a periodic electrical signal.
Spectrum Analysers
Spectrum analysers are devices that operate in the frequency domain and display power vs frequency. A plot of power against frequency is another one of the most basic measurements that can be performed on a spectrum analyser.
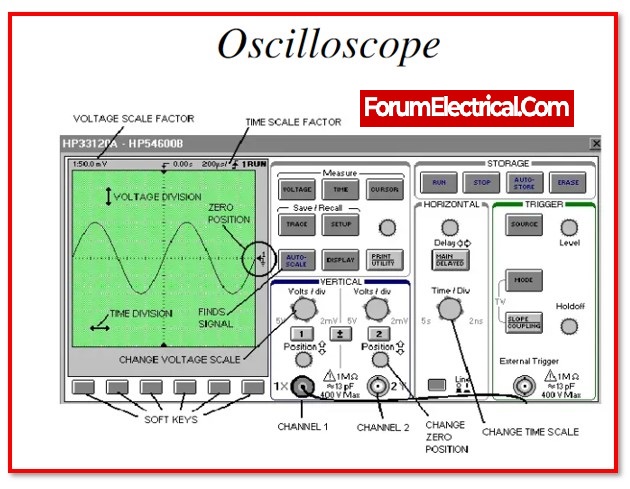
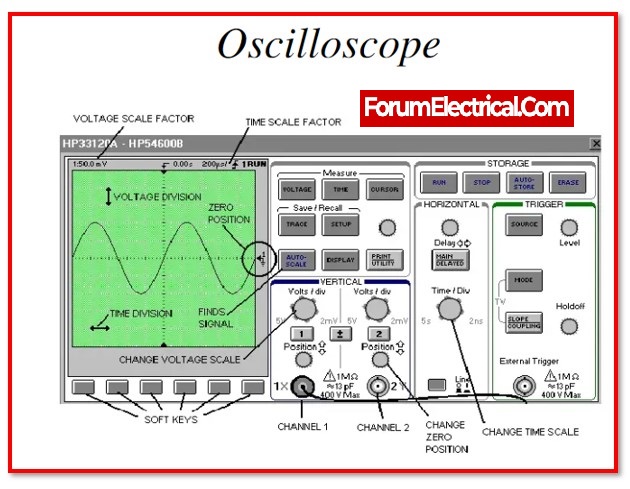
Oscilloscope
An oscilloscope, which was originally known as an oscillograph, is a type of instrument that visually represents electrical signals and demonstrates how those signals evolve over the course of time.
It does so by establishing a connection with a sensor, which is a small device that generates an electrical signal in reaction to various physical stimuli such as light, sound, and temperature.
Clamp Meter
An electrical test instrument known as a clamp meter combines a simple digital multimeter with a current sensor in a single device.
Clamps measure current. Probes measure voltage. Electrical engineers are able to measure the amount of current flowing through a circuit without having to disconnect or de-energize it owing to the hinged jaw that is made into electrical meters.
The jaws can be clamped around a wire, cable, or other conductor at any point in the system, and the current can then be measured.
Galvanometer
The term “galvanometer” refers to an electromechanical device that is used for detecting and indicating the presence of an electric current.
This functions as an actuator by generating the rotational deflection in response to the passage of current through a coil when it is positioned inside a magnetic field that is stable.
Megger
Insulating force or resistance (IR) time and environmental conditions, such as temperature, humidity, moisture, and dust particles, all contribute to a decrease in the IR quality of an electrical system.
It is also influenced badly due to the presence of electrical & mechanical stress, so it has become extremely vital to monitor the IR (Insulation resistance) of equipment at a consistent regular period to prevent any electrical shock.
Signal Analyser
A signal analyser is an instrument that evaluates the amplitude and phase of an input signal at a single frequency within the instrument’s IF bandwidth.
These measurements are taken when the signal analyser is focused on a single frequency.
It does this by using digital methods in order to decipher the relevant information that is delivered by an electrical signal.
Network Analyser
A network analyser is a device that measures electrical network properties. Since reflection and transmission of electrical networks are easier to measure at high frequencies, network analysers frequently test s-parameters, although there are additional network parameter sets such as
- y-parameters,
- z-parameters, and
- h-parameters.
Network analysers are often used to assess two-port networks like
- Amplifiers and
- Filters,
but they may also be used on networks with any number of ports.
Earth Tester
An earth tester is an electrical device used to assess the resistance between the earth & an electrical installation’s grounding system.
In electrical installations, the grounding system is an essential safety component that provides a flow path for the fault current to flow to the ground in the event of a failure, avoiding electric shocks and safeguarding the equipment.
It is also called as grounding resistance tester.