1). What is Static Electricity?
Static electricity refers to the accumulation of electric charge on the surface of materials. It occurs when two objects come into contact, causing electrons to transfer between them, creating an imbalance of charges.
2). What is Current Electricity?
The flow of electric charge, defined as electrons, via a conductor is what we refer to as current electricity. It is the type of electricity used to power devices, as it involves a continuous flow of electrons.
3). What are the 2 types of Electrical Current?
The two types of electrical current are:
4). What are the primary sources of Electricity?
The primary sources of electricity include

- Fossil fuels (coal, natural gas, oil),
- Nuclear energy,
- Renewable sources (solar, wind, hydropower, geothermal), and
- Chemical energy from batteries.
5). What are the primary types of Electricity Applications?
The main applications of electricity include
- Lighting,
- Heating,
- Cooling,
- Communication,
- Powering machines, and
- Transportation.
6). What does A.C. mean?
A.C. stands for Alternating Current, where the flow of electrons reverses direction periodically.
It is the type of electricity commonly used in homes and industries.
7). What does D.C. mean?
D.C. stands for Direct Current, where the flow of electrons moves in only one direction.
- Batteries and
- Electronic devices
typically use DC.
8). What are Conductors?
Conductors are materials that allow the free flow of electric charge, due to the presence of free electrons.
Ex: Metals like copper & aluminum
9). What are Insulators?
Insulators are materials that resist the flow of electric charge, as they have tightly bound electrons that do not move freely.
Ex: Rubber, Glass, Wood, Oil and Plastic.
10). Name five materials electricians use as conductors.
- Copper,
- Aluminum,
- Silver,
- Gold, and
- Brass
are commonly used conductors.
11). Name five materials electricians use as insulators.
- Rubber,
- Glass,
- Plastic,
- Ceramic, and
- Mica
are commonly used insulators.
12). What is Dielectric Strength?
Dielectric strength is the maximum electric field that an insulating material can withstand without breaking down (or) becoming conductive.
13). What are five important properties of a good conductor?
A good conductor should have
- High electrical conductivity,
- Low resistivity,
- High tensile strength,
- Thermal conductivity, and
- Ductility.
14). What are five essential properties of a good insulator?
A good insulator should have
- High resistivity,
- High dielectric strength,
- Thermal stability,
- Low water absorption, and
- Mechanical strength.
15). What is a Semiconductor?

A semiconductor is an element with electrical conductivity in between a conductor & an insulator.
Its conductivity can be altered by doping or external influences such as temperature and electric fields.
16). What are the two main types of semiconductors?
The two main types of semiconductors are
- n-type (negative charge carriers) and
- p-type (positive charge carriers).
17). What is Resistance?
Resistance is the opposition to electric current flow in a material.
It depends on the
- Material,
- Length,
- Cross-sectional area, and
- Temperature of the conductor.
18). What are the main classifications of resistance?
The main classifications of resistance are
- Fixed resistance,
- Variable resistance (rheostats, potentiometers), and
- Non-linear resistance (such as in diodes).
19). Which unit is used to measure resistance?
Resistance is measured in ohms (Ω).
20). What is a Resistor?
A resistor is an electrical component that restricts or controls the flow of electric current in a electrical circuit.
21). Which factors affect a conductor’s resistance?
The factors that affect a conductor’s resistance include the
- Length of the conductor,
- Cross-sectional area,
- Material, and
- Temperature.
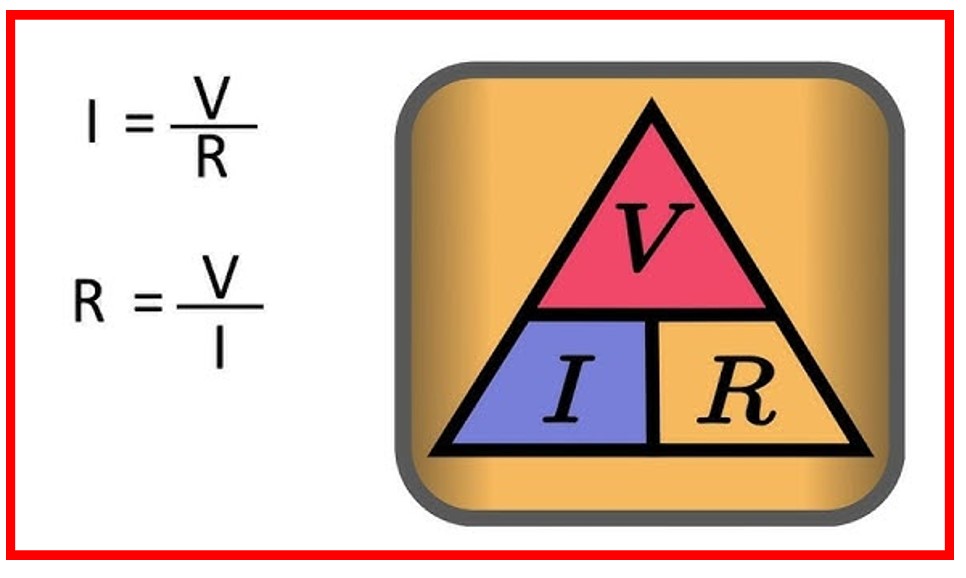
22). What is Ohm’s Law?
Ohm’s Law states that the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the two points and inversely proportional to the resistance.
Mathematically,
V=IR
where
V – Voltage
I – Current, and
R – Resistance.
23). What is Capacitance?
Capacitance is the ability of a system to store electrical energy in an electric field, measured in farads (F).
It is a property of capacitors.
24). What is Inductance?
Inductance is the ability of a conductor or coil to store energy in a magnetic field when electrical current flows through it.
It is measured in henries (H).
25). What is a Generator?
The process of converting mechanical energy into electrical energy through the use of electromagnetic induction is referred as generator.









