- Different Types of Batteries
- What are the 7 parts of a Battery?
- Preparation Essentials: Considerations Before Choosing a Battery for the Maintenance
- Regular Inspection & Maintenance
- Corrective Maintenance of Battery
- Step-by-Step Procedure for Periodic Maintenance of Battery
- Equipment Battery Maintenance Tips
- Flooded Battery Water Level Maintenance
- What is the formula for Battery Water?
- What five steps are done during Battery Maintenance?
- What four steps are done during 12 V Battery Maintenance?
- Battery Testing
- What is Cold Cranking Amp (CCA)?
Battery maintenance is recognized as an essential component of maintaining a safe and efficient warehouse.
The proper process for battery repair, on the other end, is frequently disregarded.
When it comes to conserving time, prolonging the life of your battery, and preserving your equipment, performing maintenance in the correct order is equally important as performing maintenance itself.
- Understanding battery types & charging processes is necessary for appropriate maintenance.
- Regular inspection, cleaning of terminals/cables, and following manufacturer guidelines are all essential requirements in extending battery life.
- Using equipment-specific maintenance recommendations will help you get the most out of your equipment.
Different Types of Batteries
To ensure the longevity and performance of different types of batteries, such as
- Lead-Acid Battery And
- Lithium-Ion Battery,
various maintenance procedures are required.
It is essential to understand the type of battery are working with in order to use the proper charging and maintenance procedures.
This eventually extends battery life and avoids potential problems.
1). Lead Acid Batteries
Lead-acid batteries, especially flooded lead-acid batteries, require adequate care to function properly. Regular maintenance is required to maintain these batteries clean & operating at peak performance.
These batteries require inspections every 2-4 weeks, as well as keeping adequate water levels & clean terminals.
Following the manufacturer’s charging instructions for lead-acid batteries provides maximum performance and longevity.
2). Lithium-Ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries, on the other end, require minimal (small) maintenance after the initial charge.
It is still important to monitor their state of charge on a regular basis using a monitoring tool that communicates with the integrated battery management system.
Underwriters Laboratories (UL) 1642 standard specifies the safety standards for lithium batteries, especially lithium-ion batteries, used in portable devices.
Proper charging methods, such as quickly charging the battery after each usage, will also help in the maintenance of their performance.
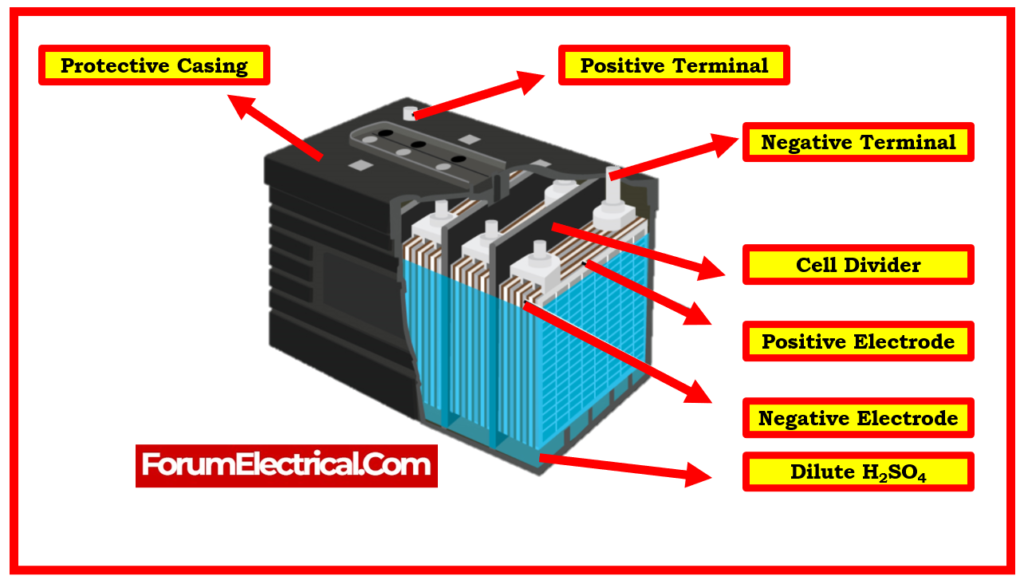
What are the 7 parts of a Battery?
A conventional battery is made up of seven different components:
- Container,
- Cathode,
- Separator,
- Anode,
- Electrodes,
- Electrolyte, and
- Collector.
Each element has a specific purpose, and when all of the parts of a battery work together, they provide the dependable & long-lasting power that depend on every day.
Preparation Essentials: Considerations Before Choosing a Battery for the Maintenance
Check the system’s voltage, battery compartment dimensions (length, breadth, and height), and energy requirements.
Select whether want to utilize a deep cycle flooded, AGM, or gel battery
Step 1: Determine the battery voltage and the number of Batteries
Based on the system’s voltage, need to determine which battery and how much to utilize to satisfy the requirements. For a 48-volt system, for example, one may connect a series of
- Eight 6V Batteries,
- Six 8V Batteries, Or
- Four 12V Batteries.
Your alternatives may be limited due to the size of the battery compartment, the performance needs, and the cost.
Allow sufficient space between batteries that allows for modest battery expansion during usage and proper airflow to maintain battery temperature down in the hot conditions.
Step 2: Select the Best Battery Model
Consider battery compartment space first when selecting a battery model, as this may limit the possibilities. Within size limitations, there may be various battery choices to choose. The volume of energy available that distinguishes these batteries.
And then consider the power requirements. When changing an existing battery, use it as a guide. If the old battery produced adequate energy, it can be changed with a battery of comparable capacity. If more energy is required, size up; if less energy is required, scale down.
Step 3: Choose the Most Effective Terminal
Finally, based on the kind of cable connections intend to utilize select which terminal option suits the requirements. Look for the available terminal(s) for the battery it’s been chosen.
Tools & Equipment Required for Inspections & Maintenance
Battery requires, at a least, the following tools & equipment:
- Digital voltmeter
- Current clamp
- Impedance tester
- System load bank
- Recorder
- Insulated socket wrenches
- Insulated box end wrenches
- Torque wrench
- Screw driver
- Rubber gloves
- Face shield or goggles
- Portable eyewash
- Fire extinguisher
Regular Inspection & Maintenance
Regular Inspection & Maintenance can assist to extend battery life. A monthly inspection is suggested to ensure peak performance.
The IEEE (Std 1188) standard specifies maintenance, testing, & replacement procedures for lead-acid batteries utilized in stationary applications. It goes over elements like visual inspection, electrical testing, & record-keeping.
- Check the battery’s charge level. Most batteries have a charge Indicator state on the top that provides an instant diagnosis of the battery’s state.
- However, a voltmeter to detect the stabilized voltage or a hydrometer to calculate the specific gravity (SG) of electrolyte is a more reliable approach to check.
- A fully charged battery will have a stabilized voltage more than 12.5 V and an SG measurement greater than 1.24 V.
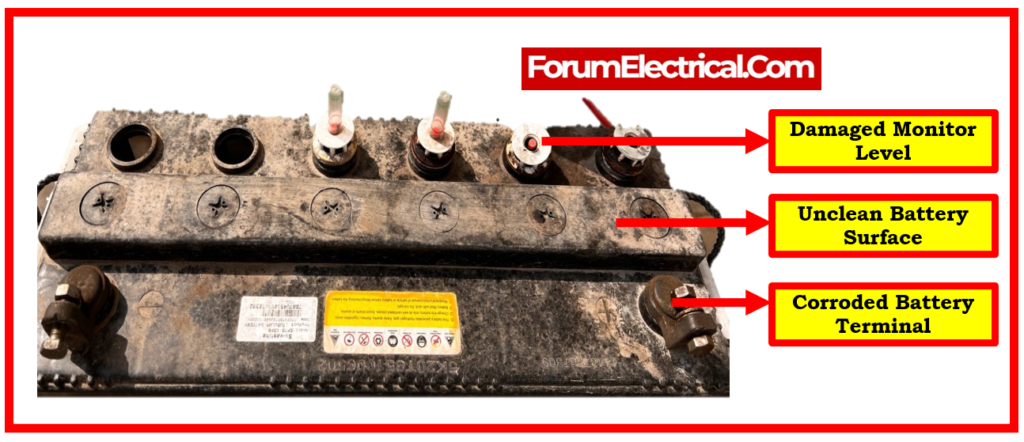
- Make sure that the battery top been kept clean, dry, and free of dirt and dust. A contaminated battery can discharge over the filth on the battery shell.
- Examine the terminals, screws, clamps, and cables for any signs of breakage, damage, or loose connections. These must be clean, tight, and corrosion-free.
- For further protection, apply a thin coat of high temperature oil to posts & cable connectors.
- Examine the battery case for noticeable physical damage (or) warpage. This usually implies that the battery has been overcharged (or) overheated.
- If have a maintenance battery, make sure that there is enough electrolyte coating the battery plates.
- If need to top up the battery, don’t overfill because the fluid levels increase when the battery is fully charged & may overflow. Fill with distilled (or) de-mineralized water only, and never with sulfuric acid.
- Check the charge indicator state when servicing a battery. This provides with an overview of the battery’s state and whether it requires to be charged (or) replaced.
- Even when the sign indicates that the battery has to be replaced, the vehicle can still start.
- If the State of Charge Indicator indicates ‘Replace Battery,’ it is essential that the battery be replaced because electrolyte levels may go below the plates, resulting in an internal explosion.
- For batteries utilized in seasonal applications & stored for an extended period of time, completely charge the battery before storing.
- Check the charge or voltage state on a regular basis. Recharge the battery if the voltage falls below 12.5V. Before reconnecting electrical devices, it is essential to thoroughly inspect the battery.
Corrective Maintenance of Battery
Step-1: When battery capacity drops to 20%, charge it
Allow the battery to down to 20% before charging. Discharging the battery’s banks too far will cause lasting damage to the battery’s performance and endurance. It can also overheat, causing the electric circuits to be damaged.
Allow the battery to charge to full capacity without interruption.
The lifespan of a battery is frequently linked to the number of charges it receives.
Undercharging, charging for a short duration of time numerous times a day (including quick charging over a lunch break), and charging before the battery has drained more than 50% of its electrical capacity can all result in a lower performance rate or a shorter battery life.
Step-2: Charge equalizer as needed
This is an intended overcharge that plenty of batteries require in order to work properly and efficiently.
If you are uncertain whether an equalizer charge is required, how frequently to administer it, or how to provide an equalizer charge, see the battery/charger manual for more information.
Batteries will charge over a longer amount of time when receiving an equalization charge. This prolonged charge time may cause over-heating; thus, batteries need to be monitored throughout the process.
Step-3: Turn off the power & let the battery cool before removing it
Do not turn off the power until the battery has achieved 100% capacity. If the battery is fully charged, it will run more effectively throughout the day.
This method will also reduce the number of periods the battery requires to be charged, extending its longevity.
The battery needs to cool before being reinstalled or it can overheat, potentially harming both the battery & the electrical circuits.
Step-4: Water the battery after charging and disconnecting when water/electrolytes are needed
It is not advisable to water the battery at any other time.
Charge before watering because charging heat may lead to changes in the water levels (both evaporation and overflow). If the water levels are very low before charging, a small amount of water may be added to protect the battery from overheating during charging process.
Step-5: Clean the battery immediately after overfilling
Overflow during this procedure will leak battery acid over the surface of the cell, causing corrosion if not cleaned immediately.
Corrosion and leftover acid can reduce battery life & cause overheating while charging and use.
Step-6: Regularly clean batteries
Surface cleaning will keep dirt, corrosion, and other problems away.
After watering, clean the batteries. This will spare customers from having to repeat a step if there is an overflow, water leaks, etc.
Always clean batteries in specified washing area, using the proper equipment and neutralizing detergent.
A specific cleanser or a simple dusting of baking soda can be used as a neutralizing agent.
Whatever method is employed, this is an important step that will neutralize any stored battery acid on the surface & prevent corrosion of the battery & nearby electrical circuits.
Establishing an adequate battery maintenance procedure is essential for ensuring a productive & safe work environment. Charts and maintenance plans are a fantastic approach to ensuring that batteries are properly maintained.
Step-by-Step Procedure for Periodic Maintenance of Battery
Battery maintenance is essential for ensuring their best performance and longevity. Specific maintenance requirements will vary depending on the type of battery; however, the following are general step-by-step procedure that apply to many different types of batteries, including lead-acid batteries typically used in cars and uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems.
Step-1: Monitor Levels
Step-2: Do Not Top Off Before Charging
Step-3 Test Battery & Charger Compatibility
Step-4 Charge Batteries 100%
Step-4: Batteries Coolness
Step-5: Monitor the BDI (Battery Discharge Indicators).
Step-6: Check Plugs, Cables, and Chargers
Step-7: Use Batteries Equally
Step-8: Maintain Lids Clean
Step-9: Ensure Safety
Step-1: Monitor Levels
Maintaining battery fluid levels is essential for maximizing battery performance.
Top up the cells so electrolyte covers the plates and separators. Manufacturers recommend checking battery levels regularly.
Preventing premature damage (or) failure is a further advantage. Always use distilled, de-ionized water to top off lead acid batteries.
Step-2: Do Not Top Off Before Charging
Fresh water must be added to batteries after they have finished charging since water is essential to energy transfer.
Electrolyte expands when warm, so replenishing up before a charge can cause spillage.
Step-3 Test Battery & Charger Compatibility
A charger that just works is different from one that is designed to charge a specific battery type and make.
Make sure battery providers are using the right charging equipment. Incorrect chargers can damage batteries & invalidate insurance.
Charge according to the charger’s instructions.
Step-4 Charge Batteries 100%
Battery performance is optimum when fully charged. Do not partially charge or interrupt a charging cycle.
Doing so may permanently damage the battery, diminishing its capacity and lifespan.
Step-4: Batteries Coolness
Most lead acid batteries need 2 hours to cool after charging. Enforce this time in the charging schedule and health & safety best practices.
Step-5: Monitor the BDI (Battery Discharge Indicators)
Equipment operators must monitor Battery Discharge Indicators. When the battery indicator reads 25%, recharge it.
Maintaining them will help the battery perform at its best for longer.
Modern machines also stop down hydraulic function at 80% discharge, prohibiting lift, but drive functions are unaffected.
Step-6: Check Plugs, Cables, and Chargers
- Plugs,
- Chargers, and
- Battery Leads
can corrode.
Check all equipment & connections for frayed wires or damaged insulation.
Weekly visual inspections will identify problems before they impede machinery functioning.
Step-7: Use Batteries Equally
Make sure that the use and charge several batteries equitably in different shift scenarios.
This prevents batteries from being over-cycled, which can reduce performance and lifespan.
Battery Monitoring System technology can notify operators of battery state and ensure even utilization.
Step-8: Maintain Lids Clean
Keep battery cell lids clean and debris-free. It will prevent ground leakage and capacity loss.
Step-9: Ensure Safety
Always wear safety gear when working with batteries. The charging area should have spill kits and eye wash stations.
When charging in location, maintain battery compartment lids open and ventilate batteries and chargers.
When not being in use, store charge cables safely to avoid damage and trip hazards.
Equipment Battery Maintenance Tips
Following these 8 battery maintenance recommendations to extend battery life and assure peak performance. These procedures might help you avoid costly downtime & keep your equipment functioning smoothly.
- Terminals and cables should be inspected and cleaned on a regular basis.
- Use appropriate charging techniques.
- Battery life should be monitored.
- Maintain a well-balanced battery pack.
- Temperature control
- Battery maintenance for the flooded batteries
- Use appropriate storage techniques.
- Maintenance of specialized equipment
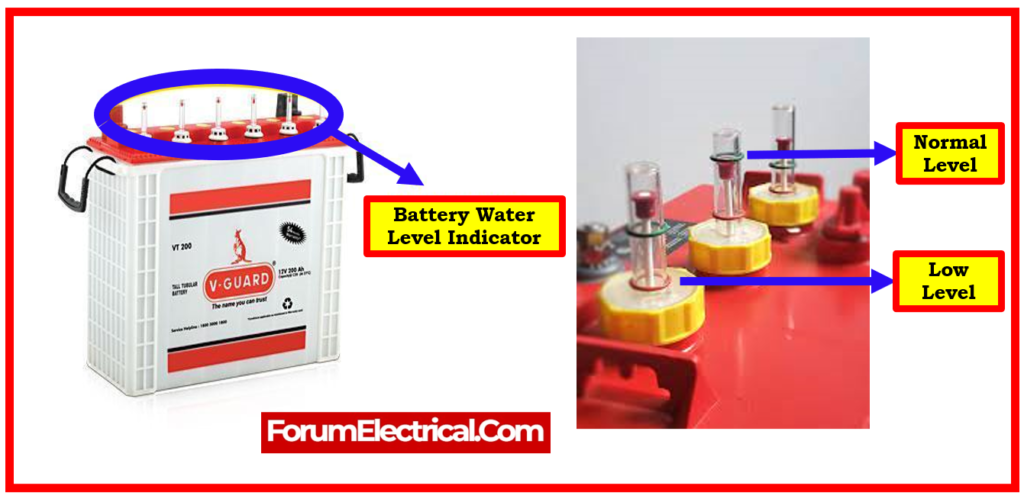
Flooded Battery Water Level Maintenance
Maintain flooded lead-acid battery water levels by utilizing distilled water & checking & replacing water levels on a regular basis.
IEEE 450 specifies procedures for maintaining, testing, and replacing lead-acid batteries.
Proper water level control is critical for flooded lead-acid battery health. Monitor the water levels a minimum of once a month and replenish as needed with distilled water.
Distilled Water
When refilling flooded lead-acid batteries, use distilled water because non-distilled water might cause damage.
Distilled water contains no minerals that can harm the battery, unlike tap water. These minerals may lead to corrosion and shorten the life of the battery.
As a result, it is essential to utilize the appropriate type of water.
Water Level Monitoring and Refilling
To keep flooded lead-acid batteries healthy, check and refill their water levels every 2-4 weeks.
Monitoring water levels on a regular basis helps to prevent problems arising from insufficient electrolyte levels & ensures the battery’s longevity.
It is essential to check & refill water levels on a frequent basis to make sure that the battery is working properly.
What is the formula for Battery Water?
Battery acid is a mixture of sulfuric acid (H2SO4) & water (H2O) with a pH of approximately 0.8 and a concentration of 4-5 mol/L. It does not have a fixed formula.
What five steps are done during Battery Maintenance?
The 5 major steps are done during battery maintenance are as follows:
- Battery should be charged.
- Maintain Fluid Levels Good. The maximum capacity of the battery is dependent on optimal water levels.
- Equilibrate the battery.
- Regulate the battery temperature.
- Clean the unit.
What four steps are done during 12 V Battery Maintenance?
- In order to ensure that battery bank charges at the appropriate voltage, should program the voltage set points.
- Every two to four weeks, or more frequently, if necessary, refill flooded lead-acid batteries with the distilled water.
- Maintain a consistent check on the battery’s level of charge
- In order to prevent corrosion, terminal connections & cables should be cleaned.
Battery Testing
Battery testing must be part of any regular maintenance schedule. Due to increased battery demands, failure warnings are minimal.
Battery replacement can reduce costs and issues with flat or dying batteries.
Fully charge a battery before testing. Even partially drained batteries can produce a misleading readout and be deemed damaged when all they need is a charge.
Many different types of testing equipment exist.
A digital battery tester is best because it’s safe, easy to use, and quickly diagnoses battery health.
- Fixed & adjustable load testers,
- Voltmeters,
- Hydrometers, and
- Discharge testers
can be used, but proper training is needed to avoid injury or vehicle damage.
Hydrometer
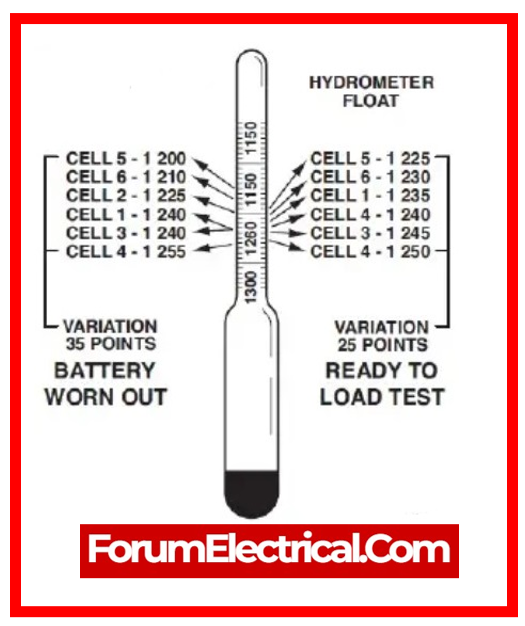
Lead acid battery state-of-charge is defined by electrolyte specific gravity (SG) (density compared to water).
Hydrometers or voltmeters can measure SG directly or indirectly by stabilized voltage. Note that acid temperature impacts results.
Digital Battery Testers
Microprocessor-controlled digital battery testers are safe, easy to use, and can detect early battery failure.
The tester sends a small signal through the battery to measure conductance (or) resistance (impedance) to determine battery state.
Adjustable Load Testers
Adjustable load testers apply a real load like cranking the engine, making them dependable for battery starting capacity testing.
This load can spark if leads are attached to corroded (or) loose terminals.
Standard testing involves loading the battery to 50% CCA for 15 seconds. Battery is good if voltage is above 9.6 volts. A 600-CCA (Cold Cranking Amps) battery must be tested at the 300CCA (Cold Cranking Amps) for 15 seconds.
The common interpretation is that the battery is good if the loaded voltage reading ranges from 9.6V and 10.6V after 15 seconds. Under 9.6V indicates a bad battery.
Constant Rate Discharge Testers
Deep Cycle batteries are often tested with discharge testers, a simple procedure.
The tester discharges the battery through a pre-set current (Amps) till it reaches a disconnect voltage. Test time is the major issue with this kind of testing.
Ex: Testing a 100 Ah battery at 5 Amps could take 20 hours.
What is Cold Cranking Amp (CCA)?
CCA is a battery industry rating that defines a battery’s ability for starting an engine in the cold temperatures. A warm environment makes simpler to start an engine than a cold one.
The number of amps that a 12-volt battery can provide at 0°F for 30 seconds while keeping a voltage of a minimum 7.2 volts is known as the rating.
The battery’s starting power increases with its CCA rating.